FoxO1 is a positive regulator of bone formation by favoring protein synthesis and resistance to oxidative stress in osteoblasts
- PMID: 20142102
- PMCID: PMC2820405
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.01.001
FoxO1 is a positive regulator of bone formation by favoring protein synthesis and resistance to oxidative stress in osteoblasts
Abstract
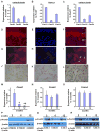
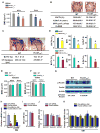
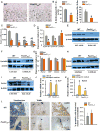
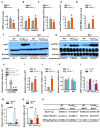
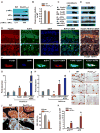
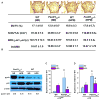
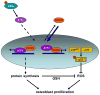
Osteoporosis, a disease of low bone mass, is associated with decreased osteoblast numbers and increased levels of oxidative stress within osteoblasts. Since transcription factors of the FoxO family confer stress resistance, we investigated their potential impact on skeletal integrity. Here we employ cell-specific deletion and molecular analyses to show that, among the three FoxO proteins, only FoxO1 is required for proliferation and redox balance in osteoblasts and thereby controls bone formation. FoxO1 regulation of osteoblast proliferation occurs through its interaction with ATF4, a transcription factor regulating amino acid import, as well as through its regulation of a stress-dependent pathway influencing p53 signaling VSports手机版. Accordingly, decreasing oxidative stress levels or increasing protein intake normalizes bone formation and bone mass in mice lacking FoxO1 specifically in osteoblasts. These results identify FoxO1 as a crucial regulator of osteoblast physiology and provide a direct mechanistic link between oxidative stress and the regulation of bone remodeling. .
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. V体育安卓版.
Figures
References
-
- Accili D, Arden KC. FoxOs at the crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and transformation. Cell. 2004;117:421–426. - PubMed
-
- Almeida M, Han L, Martin-Millan M, Plotkin LI, Stewart SA, Roberson PK, Kousteni S, O'Brien CA, Bellido T, Parfitt AM, Weinstein RS, Jilka RL, Manolagas SC. Skeletal involution by age-associated oxidative stress and its acceleration by loss of sex steroids. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:27285–27297. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arden KC. Multiple roles of FOXO transcription factors in mammalian cells point to multiple roles in cancer. Exp Gerontol. 2006;41:709–717. - PubMed (V体育官网入口)
-
- Bai XC, Lu D, Bai J, Zheng H, Ke ZY, Li XM, Luo SQ. Oxidative stress inhibits osteoblastic differentiation of bone cells by ERK and NF-kappaB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;314:197–207. - "VSports在线直播" PubMed
-
- Bouxsein ML, Melton LJ, III, Riggs BL, Muller J, Atkinson EJ, Oberg AL, Robb RA, Camp JJ, Rouleau PA, McCollough CH, Khosla S. Age- and sex-specific differences in the factor of risk for vertebral fracture: a population-based study using QCT. J Bone Miner Res. 2006;21:1475–1482. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Substances
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
Grants and funding
"V体育平台登录" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
V体育官网入口 - Miscellaneous

