Methylation of histone H3 and H4 by PRMT5 regulates ribosomal RNA gene transcription (V体育平台登录)
- PMID: 19998411
- PMCID: PMC2882297
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.22432 (V体育平台登录)
Methylation of histone H3 and H4 by PRMT5 regulates ribosomal RNA gene transcription
Abstract
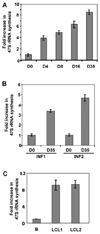
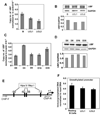
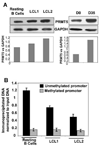
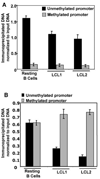
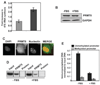
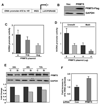
In an effort to understand the epigenetic regulation of ribosomal RNA gene (rDNA) expression we have previously demonstrated the role of DNA methyltransferases and methyl CpG binding proteins in rRNA synthesis. Here, we studied the role of protein arginine methyltransferase PRMT5 and the two methylated histones H3R8Me2 and H4R3Me2, in rDNA expression in Epstein Barr virus- transformed primary B-cells (LCLs) and in HeLa cells responding to serum-regulated growth. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay showed that histones H3 and H4 associated with rRNA promoters were differentially methylated at arginine residues 8 and 3, respectively, depending on its transcriptional activity. Association of PRMT5 and methylated H3 with the unmethylated promoters in resting B-cells was significantly reduced in rapidly growing LCLs. Unlike PRMT5 and H3R8Me2, histone H4 associated with both methylated and unmethylated rRNA promoters in resting B-cells was methylated at the R3 residue. However, a dramatic decrease in R3 methylation of H4 recruited to the unmethylated rRNA promoters was observed in LCLs while it remained unaltered in the fraction bound to the methylated promoters. Differential interaction of PRMT5 and methylation of H3 and H4 associated with the rRNA promoters was also observed when serum starved HeLa cells were allowed to grow in serum replenished media VSports手机版. Ectopic expression of PRMT5 suppressed activity of both unmethylated and methylated rRNA promoter in transient transfection assay whereas siRNA mediated knockdown of PRMT5 increased rRNA synthesis in HeLa cells. These data suggest a key role of PRMT5 and the two methylated histones in regulating rRNA promoter activity. .
(c) 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

V体育2025版 - References
-
- Ancelin K, Lange UC, Hajkova P, Schneider R, Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T, Surani MA. Blimp1 associates with Prmt5 and directs histone arginine methylation in mouse germ cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:623–630. - "VSports注册入口" PubMed
-
- Bedford MT, Richard S. Arginine methylation an emerging regulator of protein function. Mol Cell. 2005;18:263–272. - PubMed (V体育ios版)
"V体育安卓版" Publication types
- "VSports app下载" Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
Substances
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
Grants and funding
"V体育2025版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (VSports)

