V体育安卓版 - Smoking induces long-lasting effects through a monoamine-oxidase epigenetic regulation
- PMID: 19956754
- PMCID: PMC2775922
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007959
Smoking induces long-lasting effects through a monoamine-oxidase epigenetic regulation
Abstract
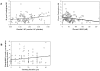
Background: Postulating that serotonin (5-HT), released from smoking-activated platelets could be involved in smoking-induced vascular modifications, we studied its catabolism in a series of 115 men distributed as current smokers (S), never smokers (NS) and former smokers (FS) who had stopped smoking for a mean of 13 years VSports手机版. .
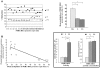
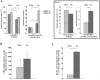
Methodology/principal findings: 5-HT, monoamine oxidase (MAO-B) activities and amounts were measured in platelets, and 5-hydroxyindolacetic acid (5-HIAA)--the 5-HT/MAO catabolite--in plasma samples. Both platelet 5-HT and plasma 5-HIAA levels were correlated with the 10-year cardiovascular Framingham relative risk (P<0. 01), but these correlations became non-significant after adjustment for smoking status, underlining that the determining risk factor among those taken into account in the Framingham risk calculation was smoking. Surprisingly, the platelet 5-HT content was similar in S and NS but lower in FS with a parallel higher plasma level of 5-HIAA in FS. This was unforeseen since MAO-B activity was inhibited during smoking (P<0. 00001). It was, however, consistent with a higher enzyme protein concentration found in S and FS than in NS (P<0. 001). It thus appears that MAO inhibition during smoking was compensated by a higher synthesis. To investigate the persistent increase in MAO-B protein concentration, a study of the methylation of its gene promoter was undertaken in a small supplementary cohort of similar subjects. We found that the methylation frequency of the MAOB gene promoter was markedly lower (P<0. 0001) for S and FS vs. NS due to cigarette smoke-induced increase of nucleic acid demethylase activity V体育安卓版. .
Conclusions/significance: This is one of the first reports that smoking induces an epigenetic modification. A better understanding of the epigenome may help to further elucidate the physiopathology and the development of new therapeutic approaches to tobacco addiction. The results could have a larger impact than cardiovascular damage, considering that MAO-dependent 5-HT catabolism is also involved in addiction, predisposition to cancer, behaviour and mental health V体育ios版. .
Conflict of interest statement (V体育ios版)
Figures
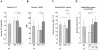
References (VSports在线直播)
-
- Page IH. Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers Inc; 1968. Serotonin.143
-
- Lewis A, Miller JH, Lea RA. Monoamine oxidase and tobacco dependence. NeuroToxicology. 2007;28:182–195. - PubMed
-
- Lan NC, Heinzmann C, Gal A, Klisak I, Orth U, et al. Human monoamine oxidase A and B genes map to Xp11.23 and are deleted in a patient with Norrie disease. Genomics. 1989;4:552–559. - PubMed (V体育官网入口)
-
- Vikenes K, Farstad M, Nordrehaug JE. Serotonin is associated with coronary artery disease and cardiac events. Circulation. 1999;100:483–489. - "V体育2025版" PubMed
Publication types
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
V体育2025版 - LinkOut - more resources
V体育官网入口 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

