WAVE1 regulates Bcl-2 localization and phosphorylation in leukemia cells
- PMID: 19890377
- PMCID: "VSports app下载" PMC2866426
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2009.224
WAVE1 regulates Bcl-2 localization and phosphorylation in leukemia cells
Abstract
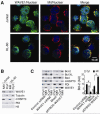
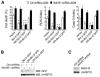
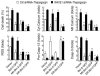
Bcl-2 proteins are over-expressed in many tumors and are critically important for cell survival. Their anti-apoptotic activities are determined by intracellular localization and post-translational modifications (such as phosphorylation). Here, we showed that WAVE1, a member of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein family, was over-expressed in blood cancer cell lines, and functioned as a negative regulator of apoptosis. Further enhanced expression of WAVE1 by gene transfection rendered leukemia cells more resistant to anti-cancer drug-induced apoptosis; whereas suppression of WAVE1 expression by RNA interference restored leukemia cells' sensitivity to anti-drug-induced apoptosis. WAVE1 was found to be associated with mitochondrial Bcl-2, and its depletion led to mitochondrial release of Bcl-2, and phosphorylation of ASK1/JNK and Bcl-2 VSports手机版. Furthermore, depletion of WAVE1 expression increased anti-cancer drug-induced production of reactive oxygen species in leukemia cells. Taken together, these results suggest WAVE1 as a novel regulator of apoptosis, and potential drug target for therapeutic intervention of leukemia. .
Figures
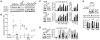

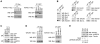
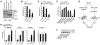
References
-
- Igney FH, Krammer PH. Death and anti-death: tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:277–288. - PubMed
-
- Herr I, Debatin KM. Cellular stress response and apoptosis in cancer therapy. Blood. 2001;98:2603–2614. - PubMed
-
- Letai AG. Diagnosing and exploiting cancer's addiction to blocks in apoptosis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:121–132. - "VSports最新版本" PubMed
-
- Rong Y, Distelhorst CW. Bcl-2 protein family members: versatile regulators of calcium signaling in cell survival and apoptosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008;70:73–91. - "VSports app下载" PubMed
-
- Vaux DL, Cory S, Adams JM. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature. 1988;335:440–442. - PubMed
VSports最新版本 - Publication types
- Actions (V体育ios版)
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
Substances
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
"VSports最新版本" Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育2025版" Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
"VSports手机版" Miscellaneous

