Biofilm formation as a novel phenotypic feature of adherent-invasive Escherichia coli (AIEC)
- PMID: 19772580
- PMCID: PMC2759958
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-202
V体育2025版 - Biofilm formation as a novel phenotypic feature of adherent-invasive Escherichia coli (AIEC)
Abstract
Background: Crohn's disease (CD) is a high morbidity chronic inflammatory disorder of unknown aetiology. Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli (AIEC) has been recently implicated in the origin and perpetuation of CD. Because bacterial biofilms in the gut mucosa are suspected to play a role in CD and biofilm formation is a feature of certain pathogenic E VSports手机版. coli strains, we compared the biofilm formation capacity of 27 AIEC and 38 non-AIEC strains isolated from the intestinal mucosa. Biofilm formation capacity was then contrasted with the AIEC phenotype, the serotype, the phylotype, and the presence of virulence genes. .
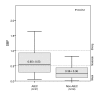
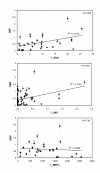
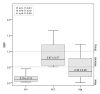
Results: Specific biofilm formation (SBF) indices were higher amongst AIEC than non-AIEC strains (P = 0. 012). In addition, 65. 4% of moderate to strong biofilms producers were AIEC, whereas 74. 4% of weak biofilm producers were non-AIEC (P = 0. 002). These data indicate that AIEC strains were more efficient biofilm producers than non-AIEC strains. Moreover, adhesion (P = 0. 009) and invasion (P = 0 V体育安卓版. 003) indices correlated positively with higher SBF indices. Additionally, motility (100%, P < 0. 001), H1 type flagellin (53. 8%, P < 0. 001), serogroups O83 (19. 2%, P = 0. 008) and O22 (26. 9%, P = 0. 001), the presence of virulence genes such as sfa/focDE (38. 5%, P = 0. 003) and ibeA (26. 9%, P = 0. 017), and B2 phylotype (80. 8%, P < 0. 001) were frequent characteristics amongst biofilm producers. .
Conclusion: The principal contribution of the present work is the finding that biofilm formation capacity is a novel, complementary pathogenic feature of the recently described AIEC pathovar. Characterization of AIEC specific genetic determinants, and the regulatory pathways, involved in biofilm formation will likely bring new insights into AIEC pathogenesis V体育ios版. .
VSports注册入口 - Figures
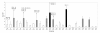
VSports手机版 - References
-
- Economou M, Pappas G. New Global Map of Crohn's Disease: Genetic, Environmental, and Socioeconomic Correlations. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14(5):709–720. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20352. - DOI (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (VSports在线直播)
Medical

