"VSports最新版本" Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II links ER stress with Fas and mitochondrial apoptosis pathways
- PMID: 19741297
- PMCID: PMC2752072
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI38857
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II links ER stress with Fas and mitochondrial apoptosis pathways
Abstract
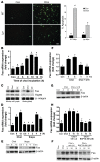
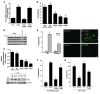
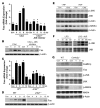
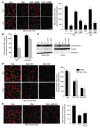
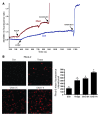
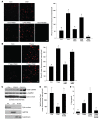
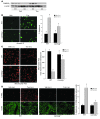
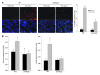
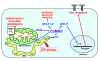
ER stress-induced apoptosis is implicated in various pathological conditions, but the mechanisms linking ER stress-mediated signaling to downstream apoptotic pathways remain unclear. Using human and mouse cell culture and in vivo mouse models of ER stress-induced apoptosis, we have shown that cytosolic calcium resulting from ER stress induces expression of the Fas death receptor through a pathway involving calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIgamma (CaMKIIgamma) and JNK. Remarkably, CaMKIIgamma was also responsible for processes involved in mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis, including release of mitochondrial cytochrome c and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. CaMKII-dependent apoptosis was also observed in a number of cultured human and mouse cells relevant to ER stress-induced pathology, including cultured macrophages, endothelial cells, and neuronal cells subjected to proapoptotic ER stress. Moreover, WT mice subjected to systemic ER stress showed evidence of macrophage mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis, renal epithelial cell apoptosis, and renal dysfunction, and these effects were markedly reduced in CaMKIIgamma-deficient mice. These data support an integrated model in which CaMKII serves as a unifying link between ER stress and the Fas and mitochondrial apoptotic pathways. Our study also revealed what we believe to be a novel proapoptotic function for CaMKII, namely, promotion of mitochondrial calcium uptake. These findings raise the possibility that CaMKII inhibitors could be useful in preventing apoptosis in pathological settings involving ER stress-induced apoptosis VSports手机版. .
"V体育官网入口" Figures

References
-
- Feng B., et al. The endoplasmic reticulum is the site of cholesterol-induced cytotoxicity in macrophages. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003;5:781–792. doi: 10.1038/ncb1035. - "VSports" DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Grants and funding
- "VSports在线直播" R01 HL079031/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL70250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States (V体育安卓版)
- R01 HL096652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS038370/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HL079031/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL087123/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075662/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States (V体育2025版)
- T32 HL007343/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- VSports app下载 - HL075662/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL087123/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- "V体育官网" HL62494/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL062494/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL007343/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
"V体育官网入口" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (VSports手机版)
Molecular Biology Databases (VSports手机版)
VSports app下载 - Research Materials
Miscellaneous

