Inhibitors of deacetylases suppress oncogenic KIT signaling, acetylate HSP90, and induce apoptosis in gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- PMID: 19706776
- PMCID: PMC2905726
- DOI: "V体育安卓版" 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4004
Inhibitors of deacetylases suppress oncogenic KIT signaling, acetylate HSP90, and induce apoptosis in gastrointestinal stromal tumors
Abstract
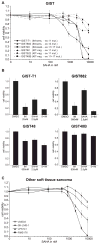
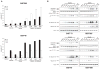
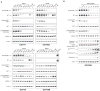
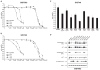
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) are characterized by activating mutations of KIT or platelet-derived growth factor receptor A (PDGFRA), and treatment with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib yields responses in the majority of patients VSports手机版. However, most patients develop secondary resistance, which is associated with a dismal prognosis. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACI) have been shown to enhance imatinib activity in imatinib-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia. Against this background, we explored whether HDACI might provide an alternative therapeutic strategy to KIT/PDGFRA kinase inhibitors in GIST. Inhibition of cell proliferation by HDACI was seen in KIT-positive but not in KIT-negative GIST cell lines, suggesting that HDACI activity is mainly conferred by targeting oncogenic KIT. KIT activity, expression, and activation of downstream pathways were strongly inhibited by several HDACI (SAHA, LBH589, VPA, trichostatin A, and NaButyrate). SAHA and LBH589 induced apoptosis in KIT-positive GIST, and strong synergism with imatinib was observed at low concentrations of SAHA and LBH589. Mechanistically, treatment with HDACI reduced KIT mRNA transcript levels and led to strong acetylation of HSP90, interfering with its activity as KIT chaperone. These results provide preclinical evidence for a disease-specific effect of HDACI in KIT-positive GIST, which could translate into therapeutic activity. .
"VSports注册入口" Figures


"VSports注册入口" References
-
- Hirota S, Nishida T, Isozaki K, et al. Gain-of-function mutation at the extracellular domain of KIT in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. J Pathol. 2001;193:505–10. - PubMed
-
- Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Duensing A, et al. PDGFRA activating mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science. 2003;299:708–10. - PubMed (VSports)
-
- Blanke CD, Demetri GD, Von Mehren M, et al. Long-term results from a randomized phase II trial of standard- versus higher-dose imatinib mesylate for patients with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors expressing KIT. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:620–5. - PubMed
-
- Demetri GD, van Oosterom AT, Garrett CR, et al. Efficacy and safety of sunitinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumour after failure of imatinib: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2006;368:1329–38. - PubMed
-
- Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Blanke CD, et al. Molecular Correlates of Imatinib Resistance in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- VSports - Actions
Substances
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育官网入口)
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

