"VSports在线直播" iBsu1103: a new genome-scale metabolic model of Bacillus subtilis based on SEED annotations
- PMID: 19555510
- PMCID: PMC2718503
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-6-r69
"V体育官网入口" iBsu1103: a new genome-scale metabolic model of Bacillus subtilis based on SEED annotations
Abstract
Background: Bacillus subtilis is an organism of interest because of its extensive industrial applications, its similarity to pathogenic organisms, and its role as the model organism for Gram-positive, sporulating bacteria. In this work, we introduce a new genome-scale metabolic model of B VSports手机版. subtilis 168 called iBsu1103. This new model is based on the annotated B. subtilis 168 genome generated by the SEED, one of the most up-to-date and accurate annotations of B. subtilis 168 available. .
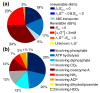
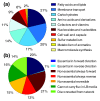
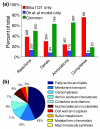
Results: The iBsu1103 model includes 1,437 reactions associated with 1,103 genes, making it the most complete model of B. subtilis available V体育安卓版. The model also includes Gibbs free energy change (DeltarG' degrees ) values for 1,403 (97%) of the model reactions estimated by using the group contribution method. These data were used with an improved reaction reversibility prediction method to identify 653 (45%) irreversible reactions in the model. The model was validated against an experimental dataset consisting of 1,500 distinct conditions and was optimized by using an improved model optimization method to increase model accuracy from 89. 7% to 93. 1%. .
Conclusions: Basing the iBsu1103 model on the annotations generated by the SEED significantly improved the model completeness and accuracy compared with the most recent previously published model. The enhanced accuracy of the iBsu1103 model also demonstrates the efficacy of the improved reaction directionality prediction method in accurately identifying irreversible reactions in the B V体育ios版. subtilis metabolism. The proposed improved model optimization methodology was also demonstrated to be effective in minimally adjusting model content to improve model accuracy. .
Figures
"V体育官网入口" References
-
- Kobayashi K, Ehrlich SD, Albertini A, Amati G, Andersen KK, Arnaud M, Asai K, Ashikaga S, Aymerich S, Bessieres P, Boland F, Brignell SC, Bron S, Bunai K, Chapuis J, Christiansen LC, Danchin A, Debarbouille M, Dervyn E, Deuerling E, Devine K, Devine SK, Dreesen O, Errington J, Fillinger S, Foster SJ, Fujita Y, Galizzi A, Gardan R, Eschevins C, et al. Essential Bacillus subtilis genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:4678–4683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0730515100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morimoto T, Kadoya R, Endo K, Tohata M, Sawada K, Liu S, Ozawa T, Kodama T, Kakeshita H, Kageyama Y, Manabe K, Kanaya S, Ara K, Ozaki K, Ogasawara N. Enhanced recombinant protein productivity by genome reduction in Bacillus subtilis. DNA Res. 2008;15:73–81. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsn002. - V体育平台登录 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
"V体育平台登录" Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
VSports最新版本 - Full Text Sources

