"VSports最新版本" p63 promotes cell survival through fatty acid synthase
- PMID: 19517019
- PMCID: PMC2691576
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005877
"V体育平台登录" p63 promotes cell survival through fatty acid synthase
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: p63 Promotes Cell Survival through Fatty Acid Synthase.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 11;14(7):e0219869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219869. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31295330 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
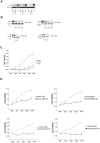
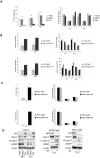
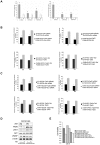
There is increasing evidence that p63, and specifically DeltaNp63, plays a central role in both development and tumorigenesis by promoting epithelial cell survival. However, few studies have addressed the molecular mechanisms through which such important function is exerted. Fatty acid synthase (FASN), a key enzyme that synthesizes long-chain fatty acids and is involved in both embryogenesis and cancer, has been recently proposed as a direct target of p53 family members, including p63 and p73. Here we show that knockdown of either total or DeltaN-specific p63 isoforms in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC9) or immortalized prostate epithelial (iPrEC) cells caused a decrease in cell viability by inducing apoptosis without affecting the cell cycle. p63 silencing significantly reduced both the expression and the activity of FASN. Importantly, stable overexpression of either FASN or myristoylated AKT (myr-AKT) was able to partially rescue cells from cell death induced by p63 silencing. FASN induced AKT phosphorylation and a significant reduction in cell viability was observed when FASN-overexpressing SCC9 cells were treated with an AKT inhibitor after p63 knockdown, indicating that AKT plays a major role in FASN-mediated survival. Activated AKT did not cause any alteration in the FASN protein levels but induced its activity, suggesting that the rescue from apoptosis documented in the p63-silenced cells expressing myr-AKT cells may be partially mediated by FASN VSports手机版. Finally, we demonstrated that p63 and FASN expression are positively associated in clinical squamous cell carcinoma samples as well as in the developing prostate. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that FASN is a functionally relevant target of p63 and is required for mediating its pro-survival effects. .
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

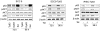
References
-
- Yang A, Kaghad M, Wang Y, Gillett E, Fleming MD, et al. p63, a p53 homolog at 3q27-29, encodes multiple products with transactivating, death-inducing, and dominant-negative activities. Mol Cell. 1998;2:305–316. - PubMed
-
- Schmale H, Bamberger C. A novel protein with strong homology to the tumor suppressor p53. Oncogene. 1997;15:1363–1367. - "VSports在线直播" PubMed
-
- Osada M, Ohba M, Kawahara C, Ishioka C, Kanamaru R, et al. Cloning and functional analysis of human p51, which structurally and functionally resembles p53. Nat Med. 1998;4:839–843. - PubMed
-
- Yang A, Schweitzer R, Sun D, Kaghad M, Walker N, et al. p63 is essential for regenerative proliferation in limb, craniofacial and epithelial development. Nature. 1999;398:714–718. - V体育安卓版 - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
MeSH terms
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
Substances
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Grants and funding (V体育安卓版)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases (V体育ios版)
Research Materials
V体育安卓版 - Miscellaneous

