Cost-effectiveness of screening for unhealthy alcohol use with % carbohydrate deficient transferrin: results from a literature-based decision analytic computer model (VSports)
- PMID: 19426168
- PMCID: PMC2758076
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.00974.x
Cost-effectiveness of screening for unhealthy alcohol use with % carbohydrate deficient transferrin: results from a literature-based decision analytic computer model
Abstract (V体育官网入口)
Background: The %carbohydrate deficient transferrin (%CDT) test offers objective evidence of unhealthy alcohol use but its cost-effectiveness in primary care conditions is unknown VSports手机版. .
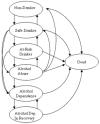
Methods: Using a decision tree and Markov model, we performed a literature-based cost-effectiveness analysis of 4 strategies for detecting unhealthy alcohol use in adult primary care patients: (i) Questionnaire Only, using a validated 3-item alcohol questionnaire; (ii) %CDT Only; (iii) Questionnaire followed by %CDT (Questionnaire-%CDT) if the questionnaire is negative; and (iv) No Screening. For those patients screening positive, clinicians performed more detailed assessment to characterize unhealthy use and determine therapy V体育安卓版. We estimated costs using Medicare reimbursement and the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. We determined sensitivity, specificity, prevalence of disease, and mortality from the medical literature. In the base case, we calculated the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) in 2006 dollars per quality-adjusted life year ($/QALY) for a 50-year-old cohort. .
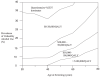
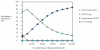
Results: In the base case, the ICER for the Questionnaire-%CDT strategy was $15,500/QALY compared with the Questionnaire Only strategy. Other strategies were dominated. When the prevalence of unhealthy alcohol use exceeded 15% and screening age was <60 years, the Questionnaire-%CDT strategy costs less than $50,000/QALY compared to the Questionnaire Only strategy V体育ios版. .
Conclusions: Adding %CDT to questionnaire-based screening for unhealthy alcohol use was cost-effective in our literature-based decision analytic model set in typical primary care conditions. Screening with %CDT should be considered for adults up to the age of 60 when the prevalence of unhealthy alcohol use is 15% or more and screening questionnaires are negative. VSports最新版本.
VSports - Figures


References
-
- Adams PF, Schoenborn CA. Health behaviors of adults: United States, 2002-2004. Vital Health Stat Ser. 2006;10:1–140. - PubMed
-
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. [Accessed June 13, 2007]. 2004. Available at: http://www.meps.ahrq.gov/mepsweb/ (V体育ios版) - PubMed
-
- Arias E. United States life tables, 2003. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2006;54:1–40. - PubMed
V体育官网入口 - Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
Substances
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

