Overexpression of peroxiredoxin 6 does not prevent ethanol-mediated oxidative stress and may play a role in hepatic lipid accumulation
- PMID: 19386791
- PMCID: PMC2700161
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.109.152983
Overexpression of peroxiredoxin 6 does not prevent ethanol-mediated oxidative stress and may play a role in hepatic lipid accumulation
Abstract (V体育ios版)
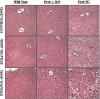
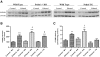
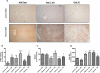
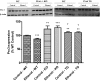
Oxidative stress is implicated in the etiology of many diseases, including alcoholic liver disease (ALD). Peroxiredoxin 6 is a cytosolic peroxidase that has been demonstrated to protect various tissues, such as skin, lung, and cardiac muscle, against acute oxidative insults. Consequently, peroxiredoxin 6 was hypothesized to also protect the liver from oxidative stress generated during the process of chronic ethanol ingestion. To test this, wild-type peroxiredoxin 6 knockout mice (KO), and transgenic peroxiredoxin 6 overexpressing mice (TG) were fed an ethanol-containing diet. Various biomarkers of ALD were assessed, along with the effects of chronic ethanol consumption on the antioxidant defenses. After 9 weeks of ethanol consumption, all backgrounds exhibited elevations of plasma alanine aminotransferase activity, hepatosteatosis, CYP2E1 induction, and lipid peroxidation; however, hepatic triglyceride accumulation seemed to be exacerbated in ethanol-fed TG mice. Differences in antioxidant protein expression and activity in response to chronic ethanol consumption were also observed. Examples include significant inductions of catalase and glutathione transferase activity in ethanol-fed KO and TG mice, along with elevated levels of glutathione peroxidase activity. These alterations in antioxidant defenses could be attributed to either compensatory responses due to the genetic manipulations or ethanol-mediated responses. In conclusion, both ethanol-fed KO and ethanol-fed TG mice developed early stage ALD and peroxiredoxin 6 may play a role in ethanol-mediated hepatic lipid accumulation. VSports手机版.
Figures


VSports最新版本 - References
-
- Albano E (2008) Oxidative mechanisms in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease. Mol Aspects Med 299 -16. - PubMed
-
- Arteel GE (2003) Oxidants and antioxidants in alcohol-induced liver disease. Gastroenterology 124778 -790. - "VSports" PubMed
-
- Arteel G, Marsano L, Mendez C, Bentley F, and McClain CJ (2003) Advances in alcoholic liver disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 17625 -647. - PubMed
-
- Bai J and Cederbaum AI (2006) Adenovirus-mediated expression of CYP2E1 produces liver toxicity in mice. Toxicol Sci 91365 -371. - PubMed (VSports最新版本)
-
- Ballatori N, Hammond CL, Cunningham JB, Krance SM, and Marchan R (2005) Molecular mechanisms of reduced glutathione transport: role of the MRP/CFTR/ABCC and OATP/SLC21A families of membrane proteins. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 204238 -255. - "VSports注册入口" PubMed
VSports注册入口 - Publication types
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
MeSH terms
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
V体育官网入口 - Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
"VSports手机版" Research Materials
Miscellaneous

