V体育官网 - Lactobacillus GG treatment ameliorates alcohol-induced intestinal oxidative stress, gut leakiness, and liver injury in a rat model of alcoholic steatohepatitis
- PMID: 19251117
- PMCID: VSports在线直播 - PMC2675276
- DOI: "VSports注册入口" 10.1016/j.alcohol.2008.12.009
"VSports注册入口" Lactobacillus GG treatment ameliorates alcohol-induced intestinal oxidative stress, gut leakiness, and liver injury in a rat model of alcoholic steatohepatitis
Abstract (VSports手机版)
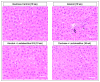
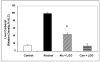
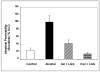
Because only 30% of alcoholics develop alcoholic liver disease (ALD), a factor other than heavy alcohol consumption must be involved in the development of alcohol-induced liver injury. Animal and human studies suggest that bacterial products, such as endotoxins, are the second key co-factors, and oxidant-mediated gut leakiness is one of the sources of endotoxemia. Probiotics have been used to prevent and treat diseases associated with gut-derived bacterial products and disorders associated with gut leakiness. Indeed, "probiotic"Lactobacillus rhamnosus has been successfully used to treat alcohol-induced liver injury in rats. However, the mechanism of action involved in the potential beneficial effects of L. rhamnosus in alcohol liver injury is not known VSports手机版. We hypothesized that probiotics could preserve normal barrier function in an animal model of ALD by preventing alcohol-induced oxidative stress and thus prevent the development of hyperpermeability and subsequent alcoholic steatohepatitis (ASH). Male Sprague-Dawley rats were gavaged with alcohol twice daily (8 gm/kg) for 10 weeks. In addition, alcoholic rats were also treated with once daily gavage of either 2. 5 x 10(7) live L. rhamnosus Gorbach-Goldin (LGG) or vehicle (V). Intestinal permeability (baseline and at 10 weeks) was determined using a sugar bolus and GC analysis of urinary sugars. Intestinal and liver tissues were analyzed for markers of oxidative stress and inflammation. In addition, livers were assessed histologically for severity of ASH and total fat (steatosis). Alcohol+LGG (ALC+LGG)-fed rats had significantly (P< or =. 05) less severe ASH than ALC+V-fed rats. L. rhamnosus Gorbach-Goldin also reduced alcohol-induced gut leakiness and significantly blunted alcohol-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in both intestine and the liver. L. rhamnosus Gorbach-Goldin probiotic gavage significantly ameliorated ASH in rats. This improvement was associated with reduced markers of intestinal and liver oxidative stress and inflammation and preserved gut barrier function. Our study provides a scientific rationale to test probiotics for treatment and/or prevention of alcoholic liver disease in man. .
Figures




"V体育官网入口" References
-
- Adachi Y, Moore LE, Bradford BU, Gao W, Thurman RG. Antibiotics prevent liver injury in rats following long-term exposure to ethanol. Gastroenterology. 1995;108:218–224. - PubMed
-
- Adawi D, Ahrne S, Molin G. Effects of different probiotic strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium on bacterial translocation and liver injury in an acute liver injury model. Int J Food Microbiol. 2001;70:213–220. - PubMed
-
- Banan A, Choudhary S, Zhang Y, Fields JZ, Keshavarzian A. Ethanol-induced barrier dysfunction and its prevention by growth factors in human intestinal monolayers: evidence for oxidative and cytoskeletal mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999;291:1075–1085. - PubMed
-
- Banan A, Fields JZ, Decker H, Zhang Y, Keshavarzian A. Nitric oxide and its metabolites mediate ethanol-induced microtubule disruption and intestinal barrier dysfunction. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;294:997–1008. - PubMed
-
- Banan A, Keshavarzian A, Zhang L, Shaikh M, Forsyth CB, Tang Y, Fields JZ. NF-kappaB activation as a key mechanism in ethanol-induced disruption of the F-actin cytoskeleton and monolayer barrier integrity in intestinal epithelium. Alcohol. 2007;41:447–460. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (VSports)
MeSH terms
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
VSports手机版 - Full Text Sources
V体育官网入口 - Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
"VSports手机版" Miscellaneous

