Human polycomb 2 protein is a SUMO E3 ligase and alleviates substrate-induced inhibition of cystathionine beta-synthase sumoylation
- PMID: 19107218
- PMCID: V体育平台登录 - PMC2606060
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004032
"VSports最新版本" Human polycomb 2 protein is a SUMO E3 ligase and alleviates substrate-induced inhibition of cystathionine beta-synthase sumoylation
Abstract
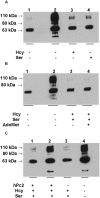
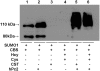
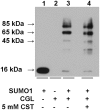
Human cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) catalyzes the first irreversible step in the transsulfuration pathway and commits homocysteine to the synthesis of cysteine. Mutations in CBS are the most common cause of severe hereditary hyperhomocysteinemia. A yeast two-hybrid approach to screen for proteins that interact with CBS had previously identified several components of the sumoylation pathway and resulted in the demonstration that CBS is a substrate for sumoylation. In this study, we demonstrate that sumoylation of CBS is enhanced in the presence of human polycomb group protein 2 (hPc2), an interacting partner that was identified in the initial yeast two-hybrid screen. When the substrates for CBS, homocysteine and serine for cystathionine generation and homocysteine and cysteine for H(2)S generation, are added to the sumoylation mixture, they inhibit the sumoylation reaction, but only in the absence of hPc2. Similarly, the product of the CBS reaction, cystathionine, inhibits sumoylation in the absence of hPc2. Sumoylation in turn decreases CBS activity by approximately 28% in the absence of hPc2 and by 70% in its presence. Based on these results, we conclude that hPc2 serves as a SUMO E3 ligase for CBS, increasing the efficiency of sumoylation. We also demonstrate that gamma-cystathionase, the second enzyme in the transsulfuration pathway is a substrate for sumoylation under in vitro conditions VSports手机版. We speculate that the role of this modification may be for nuclear localization of the cysteine-generating pathway under conditions where nuclear glutathione demand is high. .
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References (VSports)
-
- Banerjee R, Zou CG. Redox regulation and reaction mechanism of human cystathionine-beta-synthase: a PLP-dependent hemesensor protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005;433:144–156. - PubMed
-
- Miles EW, Kraus JP. Cystathionine {beta}-Synthase: Structure, Function, Regulation, and Location of Homocystinuria-causing Mutations. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:29871–29874. - PubMed
-
- Mudd SH, Levy HL, Kraus JP. Disorders of Transsulfuration. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, Vogelstein B, et al., editors. The Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies; 2001. pp. 2007–2056.
-
- Kraus JP, Janosik M, Kozich V, Mandell R, Shih V, et al. Cystathionine beta-synthase mutations in homocystinuria. Hum Mutat. 1999;13:362–375. - PubMed
Publication types (V体育官网)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
"VSports" Substances
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育官网" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
VSports - Molecular Biology Databases

