Outcomes of methotrexate therapy for psoriasis and relationship to genetic polymorphisms
- PMID: 19016697
- PMCID: VSports app下载 - PMC2680291
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08898.x
Outcomes of methotrexate therapy for psoriasis and relationship to genetic polymorphisms
Abstract
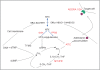
Background: The use of methotrexate is limited by interindividual variability in response. Previous studies in patients with either rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis suggest that genetic variation across the methotrexate metabolic pathway might enable prediction of both efficacy and toxicity of the drug VSports手机版. .
Objectives: To assess if single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) across four genes that are relevant to methotrexate metabolism [folypolyglutamate synthase (FPGS), gamma-glutamyl hydrolase (GGH), methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) and 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide transformylase (ATIC)] are related to treatment outcomes in patients with psoriasis V体育安卓版. .
Methods: DNA was collected from 374 patients with psoriasis who had been treated with methotrexate. Data were available on individual outcomes to therapy, namely efficacy and toxicity. Haplotype-tagging SNPs (r(2) > 0. 8) for the four genes with a minor allele frequency of > 5% were selected from the HAPMAP phase II data V体育ios版. Genotyping was undertaken using the MassARRAY spectrometric method (Sequenom). .
Results: There were no significant associations detected between clinical outcomes in patients with psoriasis treated with methotrexate and SNPs in the four genes investigated VSports最新版本. .
Conclusions: Genetic variation in four key genes relevant to the intracellular metabolism of methotrexate does not appear to predict response to methotrexate therapy in patients with psoriasis V体育平台登录. .
Figures
"V体育安卓版" References
-
- van Ede AE, Laan RF, Blom HJ, et al. The C677T mutation in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene: a genetic risk factor for methotrexate-related elevation of liver enzymes in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:2525–30. - PubMed (VSports)
-
- Urano W, Taniguchi A, Yamanaka H, et al. Polymorphisms in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene were associated with both the efficacy and the toxicity of methotrexate used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, as evidenced by single locus and haplotype analyses. Pharmacogenetics. 2002;12:183–90. - PubMed
-
- Campalani E, Arenas M, Marinaki AM, et al. Polymorphisms in folate, pyrimidine, and purine metabolism are associated with efficacy and toxicity of methotrexate in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2007;127:1860–7. - PubMed (V体育安卓版)
-
- Wessels JA, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Heijmans BT, et al. Efficacy and toxicity of methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis are associated with single-nucleotide polymorphisms in genes coding for folate pathway enzymes. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:1087–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
"VSports在线直播" Substances
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
V体育安卓版 - Miscellaneous

