MiTF regulates cellular response to reactive oxygen species through transcriptional regulation of APE-1/Ref-1 (V体育官网)
- PMID: 18971960
- PMCID: PMC4321967
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2008.255
MiTF regulates cellular response to reactive oxygen species through transcriptional regulation of APE-1/Ref-1
Abstract
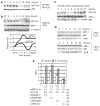
Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MiTF) is a key transcription factor for melanocyte lineage survival. Most previous work on this gene has been focused on its role in development VSports手机版. A role in carcinogenesis has emerged recently, but the mechanism is unclear. We classified melanoma cells into MiTF-positive and -negative groups and explored the function of MiTF in regulating cellular responses to reactive oxygen species (ROS). The MiTF-positive melanoma cell lines accumulated high levels of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease (APE-1/Ref-1, redox effector-1), a key redox sensor and DNA endonuclease critical for oxidative DNA damage repair. We demonstrate that APE-1 is a transcriptional target for MiTF. Knocking down MiTF led to reduced APE-1 protein accumulation, as well as abolished induction of APE-1 by ROS. MiTF-negative melanoma cells survived more poorly under ROS stress than the MiTF-positive cells based on 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay and Trypan blue staining. Overexpression of APE-1 partially rescued ROS-induced cell death when MiTF was depleted. We conclude that MiTF regulates cellular response to ROS by regulation of APE-1, and this may provide a mechanism of how MiTF is involved in melanoma carcinogenesis. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures

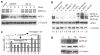


References
-
- Aksan I, Goding CR. Targeting the microphthalmia basic helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper transcription factor to a subset of E-box elements in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18:6930–8. - PMC (VSports最新版本) - PubMed
-
- Carreira S, Goodall J, Aksan I, La Rocca SA, Galibert MD, Denat L, et al. Mitf cooperates with Rb1 and activates p21Cip1 expression to regulate cell cycle progression. Nature. 2005;433:764–9. - PubMed
-
- Cen D, Gonzalez RI, Buckmeier JA, Kahlon RS, Tohidian NB, Meyskens FL., Jr Disulfiram induces apoptosis in human melanoma cells: a redox-related process. Mol Cancer Ther. 2002;1:197–204. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
V体育安卓版 - MeSH terms
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- VSports - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Substances
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Grants and funding
VSports手机版 - LinkOut - more resources
VSports最新版本 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials (VSports注册入口)
Miscellaneous

