Osteoblastic regulation of B lymphopoiesis is mediated by Gs{alpha}-dependent signaling pathways (V体育安卓版)
- PMID: 18957542
- PMCID: PMC2579363 (V体育安卓版)
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0802898105
Osteoblastic regulation of B lymphopoiesis is mediated by Gs{alpha}-dependent signaling pathways
Abstract
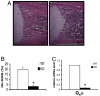
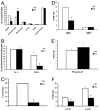
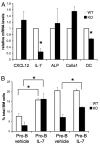
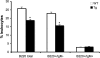
Osteoblasts play an increasingly recognized role in supporting hematopoietic development and recently have been implicated in the regulation of B lymphopoiesis. Here we demonstrate that the heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunit G(s)alpha is required in cells of the osteoblast lineage for normal postnatal B lymphocyte production. Deletion of G(s)alpha early in the osteoblast lineage results in a 59% decrease in the percentage of B cell precursors in the bone marrow VSports手机版. Analysis of peripheral blood from mutant mice revealed a 67% decrease in the number of circulating B lymphocytes by 10 days of age. Strikingly, other mature hematopoietic lineages are not decreased significantly. Mice lacking G(s)alpha in cells of the osteoblast lineage exhibit a reduction in pro-B and pre-B cells. Furthermore, interleukin (IL)-7 expression is attenuated in G(s)alpha-deficient osteoblasts, and exogenous IL-7 is able to restore B cell precursor populations in the bone marrow of mutant mice. Finally, the defect in B lymphopoiesis can be rescued by transplantation into a WT microenvironment. These findings confirm that osteoblasts are an important component of the B lymphocyte niche and demonstrate in vivo that G(s)alpha-dependent signaling pathways in cells of the osteoblast lineage extrinsically regulate bone marrow B lymphopoiesis, at least partially in an IL-7-dependent manner. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Schofield R. The relationship between the spleen colony-forming cell and the haemopoietic stem cell. Blood Cells. 1978;4:7–25. - PubMed
-
- Calvi LM, et al. Osteoblastic cells regulate the haematopoietic stem cell niche. Nature. 2003;425:841–846. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, et al. Identification of the hematopoietic stem cell niche and control of the niche size. Nature. 2003;425:836–841. - PubMed
-
- Visnjic D, et al. Hematopoiesis is severely altered in mice with an induced osteoblast deficiency. Blood. 2004;103:3258–3264. - PubMed
-
- Arai F, et al. Tie2/angiopoietin-1 signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence in the bone marrow niche. Cell. 2004;118:149–161. - PubMed
Publication types
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
Substances
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources (V体育安卓版)
Full Text Sources
V体育2025版 - Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

