"V体育平台登录" Sustained oxidative stress inhibits NF-kappaB activation partially via inactivating the proteasome
- PMID: 18948189
- PMCID: PMC2688728
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.09.021
Sustained oxidative stress inhibits NF-kappaB activation partially via inactivating the proteasome
Abstract
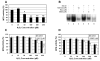
NF-kappaB is a family of important transcription factors involved in many cellular functions, such as cell survival, proliferation, and stress responses. Many studies indicate that NF-kappaB is a stress-sensitive transcription factor and its activation is regulated by reactive oxygen species VSports手机版. In previous studies, we and others demonstrated that this transcription factor can be activated by transient oxidative stress. However, the effects of sustained oxidative stress on NF-kappaB activation are not clear. The objective of this study was to determine the effects of sustained oxidative stress on NF-kappaB activation and to elucidate the signaling events affected by sustained oxidative stress. Human lens epithelial cells (HLEC) that were subjected to 4 h of continuous influx of hydrogen peroxide were used to investigate the effects of sustained oxidative stress on NF-kappaB activation. The data showed that, unlike transient oxidative stress, sustained exposure of HLEC to physiologically relevant levels of H(2)O(2) (50-100 microM for 4 h) did not induce the degradation of I-kappaB and activation of NF-kappaB, but attenuated TNFalpha-induced degradation of I-kappaB and activation of NF-kappaB. Sustained exposure of HLEC to these levels of H(2)O(2) also inactivated proteasome activity by 50-80%. Consistent with the role of the proteasome in degradation of I-kappaB and activation of NF-kappaB, treatment of HLEC with proteasome inhibitors also attenuated TNFalpha-induced I-kappaB degradation and NF-kappaB activation. The data also indicate that activation of NF-kappaB is essential for the cells to recover from oxidative stress. Inhibiting NF-kappaB activation during recovery from transient oxidative stress significantly reduced the cell viability. Together, these data indicate that sustained oxidative stress may inactivate the proteasome and subsequently inhibit NF-kappaB activation by impeding the degradation of I-kappaB. The oxidative inactivation of the proteasome and subsequent impairment of NF-kappaB activation may contribute to the death of lens epithelial cells, a common feature associated with cataract. .
VSports手机版 - Figures



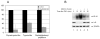

References
-
- Ghosh S, May MJ, Kopp EB. NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:225–260. - VSports手机版 - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 2008;132:344–362. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 2004;18:2195–2224. - PubMed
-
- Pasparakis M, Luedde T, Schmidt-Supprian M. Dissection of the NF-kappaB signalling cascade in transgenic and knockout mice. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:861–872. - "VSports在线直播" PubMed
-
- Perkins ND, Gilmore TD. Good cop, bad cop: the different faces of NF-kappaB. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:759–772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
Substances (V体育官网)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (VSports注册入口)

