"V体育2025版" Antiviral responses of human Leydig cells to mumps virus infection or poly I:C stimulation
- PMID: 18567898
- PMCID: VSports最新版本 - PMC2517156
- DOI: 10.1093/humrep/den207
Antiviral responses of human Leydig cells to mumps virus infection or poly I:C stimulation
Abstract
Background: The immuno-privileged status of the testis is essential to the maintenance of its functions, and innate immunity is likely to play a key role in limiting harmful viral infections, as demonstrated in the rat VSports手机版. In men mumps virus infects Leydig cells and has deleterious effects on testosterone production and spermatogenesis. The aim of this study was to test whether mumps virus infection of isolated human Leydig cells was associated with an inhibition of their innate antiviral defences. .
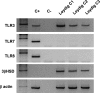
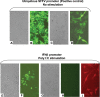
Methods: Leydig cell production of mRNA and protein for interferons (IFNs) and of three antiviral proteins-2'5' oligoadenylate synthetase (2'5'OAS), double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase (PKR) and MxA-was investigated, in the absence or presence of mumps virus or viral stimuli including poly I:C, a mimetic of RNA viruses replication product. V体育安卓版.
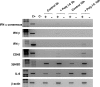
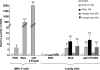
Results: Stimulated or not, human Leydig cells appeared unable to produce routinely detectable IFNs alpha, beta and gamma. Although the level of PKR remained unchanged after stimulation, the expression of 2'5'OAS and MxA was enhanced following either mumps virus or poly I:C exposure (P < 0. 05 versus control) V体育ios版. .
Conclusions: Overall, our results demonstrate that mumps virus replication in human Leydig cells is not associated with a specific inhibition of IFNs or 2'5'OAS, MxA and PKR production and that these cells display relatively weak endogenous antiviral abilities, as opposed to their rat counterparts VSports最新版本. .
Figures

References
-
- Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature. 2001;413:732–738. - PubMed
-
- Anthony CT, Skinner MK. Cytochemical and biochemical characterization of testicular peritubular myoid cells. Biol Reprod. 1989;40:811–823. - "VSports注册入口" PubMed
-
- Barlow DP, Randle BJ, Burke DC. Interferon synthesis in the early post-implantation mouse embryo. Differentiation. 1984;27:229–235. - PubMed
-
- Bigazzi PL, Barron AL, Flanagan TD, Andrada JA, Witebsky E. Growth of mumps virus in organ cultures of rhesus testis. J Infect Dis. 1968;118:411–421. - PubMed
-
- Bjorvatn B. Mumps virus recovered from testicles by fine-needle aspiration biopsy in cases of mumps orchitis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1973;5:3–5. - PubMed
Publication types (V体育官网)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
"V体育官网" MeSH terms
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Substances (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)

