Vorinostat inhibits STAT6-mediated TH2 cytokine and TARC production and induces cell death in Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines
- PMID: 18541724
- PMCID: PMC2515130
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-01-133769
Vorinostat inhibits STAT6-mediated TH2 cytokine and TARC production and induces cell death in Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines
Abstract
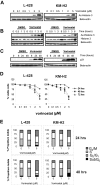
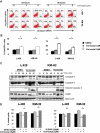
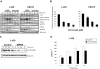
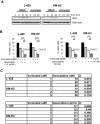
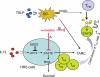
Epigenetic changes have been implicated in silencing several B-cell genes in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells (HRS) of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), and this mechanism has been proposed to promote HRS survival and escape from immunosurveillance. However, the molecular and functional consequences of histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition in HL have not been previously described VSports手机版. In this study, we report that the HDAC inhibitor vorinostat induced p21 expression and decreased Bcl-xL levels causing cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. Furthermore, vorinostat inhibited STAT6 phosphorylation and decreased its mRNA levels in a dose- and time-dependent manner, which was associated with a decrease in the expression and secretion of Thymus and Activation-Regulated Chemokine (TARC/CCL17) and interleukin (IL)-5 and an increase in IP-10 levels. Moreover, vorino-stat inhibited TARC secretion by dendritic cells that were activated by the thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP). Collectively, these data suggest that pharmacologic HDAC inhibition in HL may induce favorable antitumor activity by a direct antiproliferative effect on HRS cells, and possibly by an immune mediated effect by altering cytokine and chemokines secretion in the microenvironment. .
Figures


VSports app下载 - References
-
- Skinnider BF, Mak TW. The role of cytokines in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2002;99:4283–4297. - V体育安卓版 - PubMed
-
- Re D, Thomas RK, Behringer K, Diehl V. From Hodgkin disease to Hodgkin lymphoma: biologic insights and therapeutic potential. Blood. 2005;105:4553–4560. - PubMed (VSports注册入口)
-
- Baus D, Pfitzner E. Specific function of STAT3, SOCS1, and SOCS3 in the regulation of proliferation and survival of classical Hodgkin lymphoma cells. Int J Cancer. 2006;118:1404–1413. - PubMed
-
- Cochet O, Frelin C, Peyron JF, Imbert V. Constitutive activation of STAT proteins in the HDLM-2 and L540 Hodgkin lymphoma-derived cell lines supports cell survival. Cell Signal. 2006;18:449–455. - PubMed
-
- Skinnider BF, Elia AJ, Gascoyne RD, et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 is frequently activated in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2002;99:618–626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
"V体育安卓版" Substances
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports" Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous (VSports注册入口)

