Vorinostat synergistically potentiates MK-0457 lethality in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells sensitive and resistant to imatinib mesylate
- PMID: 18505786
- PMCID: "V体育2025版" PMC2481545
- DOI: "VSports手机版" 10.1182/blood-2007-10-116376
V体育官网 - Vorinostat synergistically potentiates MK-0457 lethality in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells sensitive and resistant to imatinib mesylate
Abstract
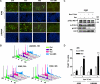
Interactions between the dual Bcr/Abl and aurora kinase inhibitor MK-0457 and the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat were examined in Bcr/Abl(+) leukemia cells, including those resistant to imatinib mesylate (IM), particularly those with the T315I mutation. Coadministration of vorinostat dramatically increased MK-0457 lethality in K562 and LAMA84 cells. Notably, the MK-0457/vorinostat regimen was highly active against primary CD34(+) chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) cells and Ba/F3 cells bearing various Bcr/Abl mutations (ie, T315I, E255K, and M351T), as well as IM-resistant K562 cells exhibiting Bcr/Abl-independent, Lyn-dependent resistance. These events were associated with inactivation and down-regulation of wild-type (wt) and mutated Bcr/Abl (particularly T315I) VSports手机版. Moreover, treatment with MK-0457 resulted in accumulation of cells with 4N or more DNA content, whereas coadministration of vorinostat markedly enhanced aurora kinase inhibition by MK-0457, and preferentially killed polyploid cells. Furthermore, vorinostat also interacted with a selective inhibitor of aurora kinase A and B to potentiate apoptosis without modifying Bcr/Abl activity. Finally, vorinostat markedly induced Bim expression, while blockade of Bim induction by siRNA dramatically diminished the capacity of this agent to potentiate MK-0457 lethality. Together, these findings indicate that vorinostat strikingly increases MK-0457 activity against IM-sensitive and -resistant CML cells through inactivation of Bcr/Abl and aurora kinases, as well as by induction of Bim. .
Figures
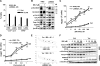
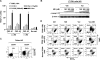
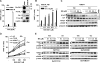



References
-
- Druker BJ, O'Brien SG, Cortes J, Radich J. Chronic myelogenous leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2002:111–135. - PubMed
-
- Bedi A, Zehnbauer BA, Barber JP, Sharkis SJ, Jones RJ. Inhibition of apoptosis by BCR-ABL in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1994;83:2038–2044. - PubMed
-
- Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O'Brien SG, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2408–2417. - PubMed
-
- Mughal TI, Goldman JM. Chronic myeloid leukemia: current status and controversies. Oncology (Williston Park) 2004;18:837–844. 847. - PubMed
-
- Ritchie E, Nichols G. Mechanisms of resistance to imatinib in CML patients: a paradigm for the advantages and pitfalls of molecularly targeted therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2006;6:645–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Substances
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

