V体育ios版 - "Re-educating" tumor-associated macrophages by targeting NF-kappaB
- PMID: 18490490
- PMCID: PMC2413024
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20080108
"Re-educating" tumor-associated macrophages by targeting NF-kappaB (V体育官网入口)
Abstract
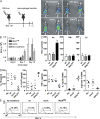
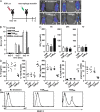
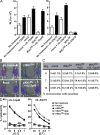
The nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) signaling pathway is important in cancer-related inflammation and malignant progression. Here, we describe a new role for NF-kappaB in cancer in maintaining the immunosuppressive phenotype of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). We show that macrophages are polarized via interleukin (IL)-1R and MyD88 to an immunosuppressive "alternative" phenotype that requires IkappaB kinase beta-mediated NF-kappaB activation. When NF-kappaB signaling is inhibited specifically in TAMs, they become cytotoxic to tumor cells and switch to a "classically" activated phenotype; IL-12(high), major histocompatibility complex II(high), but IL-10(low) and arginase-1(low) VSports手机版. Targeting NF-kappaB signaling in TAMs also promotes regression of advanced tumors in vivo by induction of macrophage tumoricidal activity and activation of antitumor activity through IL-12-dependent NK cell recruitment. We provide a rationale for manipulating the phenotype of the abundant macrophage population already located within the tumor microenvironment; the potential to "re-educate" the tumor-promoting macrophage population may prove an effective and novel therapeutic approach for cancer that complements existing therapies. .
"VSports手机版" Figures


VSports在线直播 - Comment in
-
VSports在线直播 - IKKbeta/NF-kappaB and the miscreant macrophage.J Exp Med. 2008 Jun 9;205(6):1255-9. doi: 10.1084/jem.20081056. Epub 2008 Jun 2. J Exp Med. 2008. PMID: 18519650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Condeelis, J., and J.W. Pollard. 2006. Macrophages: obligate partners for tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Cell. 124:263–266. - PubMed
-
- Sica, A., T. Schioppa, A. Mantovani, and P. Allavena. 2006. Tumour-associated macrophages are a distinct M2 polarised population promoting tumour progression: potential targets of anti-cancer therapy. Eur. J. Cancer. 42:717–727. - "V体育官网入口" PubMed
-
- Gordon, S. 2003. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3:23–35. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill, F., K.A. Charles, and A. Mantovani. 2005. Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of malignant disease. Cancer Cell. 7:211–217. - PubMed
-
- Mantovani, A., A. Sica, S. Sozzani, P. Allavena, A. Vecchi, and M. Locati. 2004. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 25:677–686. - V体育安卓版 - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育官网" Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育官网" Actions
Substances
Grants and funding
V体育ios版 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases (V体育2025版)
Research Materials

