Persistent activation of an innate immune response translates respiratory viral infection into chronic lung disease
- PMID: 18488036
- PMCID: PMC2575848
- DOI: 10.1038/nm1770 (V体育安卓版)
"V体育官网入口" Persistent activation of an innate immune response translates respiratory viral infection into chronic lung disease
Abstract (V体育平台登录)
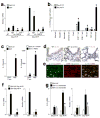
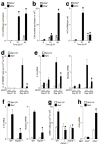
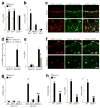
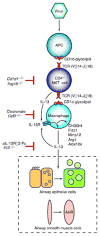
To understand the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory disease, we analyzed an experimental mouse model of chronic lung disease with pathology that resembles asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in humans. In this model, chronic lung disease develops after an infection with a common type of respiratory virus is cleared to only trace levels of noninfectious virus. Chronic inflammatory disease is generally thought to depend on an altered adaptive immune response. However, here we find that this type of disease arises independently of an adaptive immune response and is driven instead by interleukin-13 produced by macrophages that have been stimulated by CD1d-dependent T cell receptor-invariant natural killer T (NKT) cells. This innate immune axis is also activated in the lungs of humans with chronic airway disease due to asthma or COPD VSports手机版. These findings provide new insight into the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory disease with the discovery that the transition from respiratory viral infection into chronic lung disease requires persistent activation of a previously undescribed NKT cell-macrophage innate immune axis. .
VSports最新版本 - Figures


Comment in
-
Lung NKT cell commotion takes your breath away.Nat Med. 2008 Jun;14(6):609-10. doi: 10.1038/nm0608-609. Nat Med. 2008. PMID: 18535574 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mattner J, et al. Exogenous and endogenous glycolipid antigens activate NKT cells during microbial infections. Nature. 2005;434:525–529. - PubMed
-
- Seino K, Taniguchi M. Functional roles of NKT cells in the immune system. Frontiers Biosci. 2006;9:2577–2587. - PubMed
-
- Busse WW, Lemanske RFJ. Asthma. New Engl J Med. 2001;344:350–362. - PubMed
-
- Herrick CA, Bottomly K. To respond or not to respond: T cells in allergic asthma. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Jones EY, Fugger L, Strominger JL, Siebold C. MHC Class II proteins and disease: a structural perspective. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:271–282. - PubMed
V体育官网入口 - Publication types
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
Substances
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
"V体育安卓版" Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
V体育2025版 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"V体育安卓版" Medical
Molecular Biology Databases (V体育ios版)

