"V体育官网入口" NetMHC-3.0: accurate web accessible predictions of human, mouse and monkey MHC class I affinities for peptides of length 8-11
- PMID: 18463140
- PMCID: PMC2447772
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn202
V体育ios版 - NetMHC-3.0: accurate web accessible predictions of human, mouse and monkey MHC class I affinities for peptides of length 8-11
"VSports app下载" Abstract
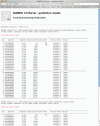
NetMHC-3. 0 is trained on a large number of quantitative peptide data using both affinity data from the Immune Epitope Database and Analysis Resource (IEDB) and elution data from SYFPEITHI. The method generates high-accuracy predictions of major histocompatibility complex (MHC): peptide binding. The predictions are based on artificial neural networks trained on data from 55 MHC alleles (43 Human and 12 non-human), and position-specific scoring matrices (PSSMs) for additional 67 HLA alleles. As only the MHC class I prediction server is available, predictions are possible for peptides of length 8-11 for all 122 alleles. artificial neural network predictions are given as actual IC(50) values whereas PSSM predictions are given as a log-odds likelihood scores. The output is optionally available as download for easy post-processing. The training method underlying the server is the best available, and has been used to predict possible MHC-binding peptides in a series of pathogen viral proteomes including SARS, Influenza and HIV, resulting in an average of 75-80% confirmed MHC binders. Here, the performance is further validated and benchmarked using a large set of newly published affinity data, non-redundant to the training set. The server is free of use and available at: http://www. cbs. dtu VSports手机版. dk/services/NetMHC. .
Figures


References
-
- Nielsen M, Lundegaard C, Worning P, Hvid CS, Lamberth K, Buus S, Brunak S, Lund O. Improved prediction of MHC class I and class II epitopes using a novel Gibbs sampling approach. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:1388–1397. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen M, Lundegaard C, Worning P, Lauemoller SL, Lamberth K, Buus S, Brunak S, Lund O. Reliable prediction of T-cell epitopes using neural networks with novel sequence representations. Protein Sci. 2003;12:1007–1017. - "V体育官网" PMC - PubMed
-
- Peters B, Bui HH, Frankild S, Nielson M, Lundegaard C, Kostem E, Basch D, Lamberth K, Harndahl M, Fleri W, et al. A community resource benchmarking predictions of peptide binding to MHC-I molecules. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2006;2:e65. - VSports app下载 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
MeSH terms
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
Substances
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
Grants and funding
V体育安卓版 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育官网入口)
Other Literature Sources
Medical
"V体育安卓版" Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

