Role for DNA polymerase kappa in the processing of N2-N2-guanine interstrand cross-links (VSports最新版本)
- PMID: 18434313
- PMCID: PMC2427349
- DOI: V体育官网 - 10.1074/jbc.M801238200
Role for DNA polymerase kappa in the processing of N2-N2-guanine interstrand cross-links
VSports手机版 - Abstract
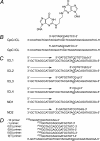
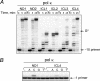
Although there exists compelling genetic evidence for a homologous recombination-independent pathway for repair of interstrand cross-links (ICLs) involving translesion synthesis (TLS), biochemical support for this model is lacking. To identify DNA polymerases that may function in TLS past ICLs, oligodeoxynucleotides were synthesized containing site-specific ICLs in which the linkage was between N(2)-guanines, similar to cross-links formed by mitomycin C and enals. Here, data are presented that mammalian cell replication of DNAs containing these lesions was approximately 97% accurate. Using a series of oligodeoxynucleotides that mimic potential intermediates in ICL repair, we demonstrate that human polymerase (pol) kappa not only catalyzed accurate incorporation opposite the cross-linked guanine but also replicated beyond the lesion, thus providing the first biochemical evidence for TLS past an ICL. The efficiency of TLS was greatly enhanced by truncation of both the 5 ' and 3 ' ends of the nontemplating strand. Further analyses showed that although yeast Rev1 could incorporate a dCTP opposite the cross-linked guanine, no evidence was found for TLS by pol zeta or a pol zeta/Rev1 combination. Because pol kappa was able to bypass these ICLs, biological evidence for a role for pol kappa in tolerating the N(2)-N(2)-guanine ICLs was sought; both cell survival and chromosomal stability were adversely affected in pol kappa-depleted cells following mitomycin C exposure. Thus, biochemical data and cellular studies both suggest a role for pol kappa in the processing of N(2)-N(2)-guanine ICLs VSports手机版. .
VSports app下载 - Figures
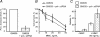


References
Publication types
V体育2025版 - MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
Substances
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports手机版" Other Literature Sources
"V体育官网入口" Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

