In vivo response to methotrexate forecasts outcome of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and has a distinct gene expression profile
- PMID: 18416598
- PMCID: PMC2292747
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050083
In vivo response to methotrexate forecasts outcome of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and has a distinct gene expression profile
"VSports手机版" Abstract
Background: Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common cancer in children, and can now be cured in approximately 80% of patients. Nevertheless, drug resistance is the major cause of treatment failure in children with ALL. The drug methotrexate (MTX), which is widely used to treat many human cancers, is used in essentially all treatment protocols worldwide for newly diagnosed ALL. Although MTX has been extensively studied for many years, relatively little is known about mechanisms of de novo resistance in primary cancer cells, including leukemia cells. This lack of knowledge is due in part to the fact that existing in vitro methods are not sufficiently reliable to permit assessment of MTX resistance in primary ALL cells. Therefore, we measured the in vivo antileukemic effects of MTX and identified genes whose expression differed significantly in patients with a good versus poor response to MTX VSports手机版. .
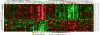
Methods and findings: We utilized measures of decreased circulating leukemia cells of 293 newly diagnosed children after initial "up-front" in vivo MTX treatment (1 g/m(2)) to elucidate interpatient differences in the antileukemic effects of MTX. To identify genomic determinants of these effects, we performed a genome-wide assessment of gene expression in primary ALL cells from 161 of these newly diagnosed children (1-18 y). We identified 48 genes and two cDNA clones whose expression was significantly related to the reduction of circulating leukemia cells after initial in vivo treatment with MTX. This finding was validated in an independent cohort of children with ALL V体育安卓版. Furthermore, this measure of initial MTX in vivo response and the associated gene expression pattern were predictive of long-term disease-free survival (p < 0. 001, p = 0. 02). .
Conclusions: Together, these data provide new insights into the genomic basis of MTX resistance and interpatient differences in MTX response, pointing to new strategies to overcome MTX resistance in childhood ALL V体育ios版. .
Trial registrations: Total XV, Therapy for Newly Diagnosed Patients With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, http://www VSports最新版本. ClinicalTrials. gov (NCT00137111); Total XIIIBH, Phase III Randomized Study of Antimetabolite-Based Induction plus High-Dose MTX Consolidation for Newly Diagnosed Pediatric Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia at Intermediate or High Risk of Treatment Failure (NCI-T93-0101D); Total XIIIBL, Phase III Randomized Study of Antimetabolite-Based Induction plus High-Dose MTX Consolidation for Newly Diagnosed Pediatric Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia at Lower Risk of Treatment Failure (NCI-T93-0103D). .
"VSports最新版本" Conflict of interest statement
Figures




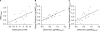
References
-
- Pui CH, Evans WE. Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:166–178. - PubMed
-
- Pui CH, Relling MV, Downing JR. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1535–1548. - PubMed (V体育官网入口)
-
- Evans WE, Relling MV. Moving towards individualized medicine with pharmacogenomics. Nature. 2004;429:464–468. - PubMed
-
- Cheok MH, Evans WE. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a model for the pharmacogenomics of cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:117–129. - PubMed
-
- Holleman A, Cheok MH, den Boer ML, Yang W, Veerman AJ, et al. Gene-expression patterns in drug-resistant acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells and response to treatment. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:533–542. - "V体育官网入口" PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases (VSports最新版本)

