Prognostic significance of cortactin levels in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: comparison with epidermal growth factor receptor status
- PMID: 18268492
- PMCID: PMC2266845
- DOI: "V体育官网" 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604245
Prognostic significance of cortactin levels in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: comparison with epidermal growth factor receptor status
Abstract
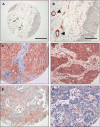
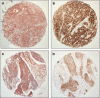
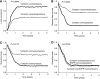
Cortactin is an actin-binding Src substrate involved in cell motility and invasion. In this study, we sought to examine the prognostic importance of cortactin protein expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). To do so, cortactin and EGF receptor (EGFR) expression was retrospectively evaluated by immunohistochemistry in a tissue microarray composed of 176 HNSCCs with a mean follow-up time of 5 years. Cortactin immunoreactivity was weak to absent in normal epithelial tissue VSports手机版. Overexpression of the protein in 77 out of 176 tumours (44%) was associated with more advanced tumour-node-metastasis stage and higher histologic grade. Cortactin overexpression was associated with significantly increased local recurrence rates (49 vs 28% for high and low expressing carcinomas, respectively), decreased disease-free survival (17 vs 61%), and decreased the 5-year overall survival of (21 vs 58%), independently of the EGFR status. In multivariate analysis, cortactin expression status remained an independent prognostic factor for local recurrence, disease-free survival, and overall survival. Importantly, we identified a subset of patients with cortactin-overexpressing tumours that displayed low EGFR levels and a survival rate that equalled that of patients with tumoral overexpression of both EGFR and cortactin. These findings identify cortactin as a relevant prognostic marker and may have implications for targeted therapies in patients with HNSCC. .
Figures
References
-
- Artym VV, Zhang Y, Seillier-Moiseiwitsch F, Yamada KM, Mueller SC (2006) Dynamic interactions of cortactin and membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase at invadopodia: defining the stages of invadopodia formation and function. Cancer Res 66: 3034–3043 - PubMed
-
- Astsaturov I, Cohen RB, Harari P (2006a) Targeting epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in the treatment of head and neck cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 6: 1179–1193 - PubMed
-
- Astsaturov I, Cohen RB, Harari PM (2006b) EGFR-targeting monoclonal antibodies in head and neck cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 6: 691–710 - PubMed
-
- Brookes S, Lammie GA, Schuuring E, de Boer C, Michalides R, Dickson C, Peters G (1993) Amplified region of chromosome band 11q13 in breast and squamous cell carcinomas encompasses three CpG islands telomeric of FGF3, including the expressed gene EMS1. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 6: 222–231 - PubMed
-
- Chuma M, Sakamoto M, Yasuda J, Fujii G, Nakanishi K, Tsuchiya A, Ohta T, Asaka M, Hirohashi S (2004) Overexpression of cortactin is involved in motility and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 41: 629–636 - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育2025版 - Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- VSports - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
Substances
- "V体育官网" Actions
V体育ios版 - LinkOut - more resources
V体育官网 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

