Caspase-14 reveals its secrets (VSports手机版)
- PMID: 18250198
- PMCID: "VSports在线直播" PMC2234247
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200709098
Caspase-14 reveals its secrets
Abstract
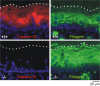
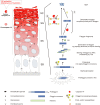
Caspase-14 is a unique member of the evolutionarily conserved family of cysteinyl aspartate-specific proteinases, which are mainly involved in inflammation and apoptosis. However, recent evidence also implicates these proteases in proliferation and differentiation. Although most caspases are ubiquitously expressed, caspase-14 expression is confined mainly to cornifying epithelia, such as the skin. Moreover, caspase-14 activation correlates with cornification, indicating that it plays a role in terminal keratinocyte differentiation VSports手机版. The determination of in vitro conditions for caspase-14 activity paved the way to identifying its substrates. The recent development of caspase-14-deficient mice underscored its importance in the correct degradation of (pro)filaggrin and in the formation of the epidermal barrier that protects against dehydration and UVB radiation. Here, we review the current knowledge on caspase-14 in skin homeostasis and disease. .
Figures


"VSports app下载" References
-
- Ahmad, M., S.M. Srinivasula, R. Hegde, R. Mukattash, T. Fernandes-Alnemri, and E.S. Alnemri. 1998. Identification and characterization of murine caspase-14, a new member of the caspase family. Cancer Res. 58:5201–5205. - PubMed
-
- Alibardi, L. 2003. Adaptation to the land: the skin of reptiles in comparison to that of amphibians and endotherm amniotes. J. Exp. Zoolog. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 298:12–41. - PubMed
-
- Alibardi, L., M. Dockal, C. Reinisch, E. Tschachler, and L. Eckhart. 2004. Ultrastructural localization of caspase-14 in human epidermis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 52:1561–1574. - PubMed
-
- Alibardi, L., E. Tschachler, and L. Eckhart. 2005. Distribution of caspase-14 in epidermis and hair follicles is evolutionarily conserved among mammals. Anat. Rec. A Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol. 286:962–973. - PubMed
-
- Arnott, C.H., K.A. Scott, R.J. Moore, A. Hewer, D.H. Phillips, P. Parker, F.R. Balkwill, and D.M. Owens. 2002. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha mediates tumour promotion via a PKC alpha- and AP-1-dependent pathway. Oncogene. 21:4728–4738. - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育ios版 - Actions
VSports在线直播 - MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Substances
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (VSports最新版本)
Molecular Biology Databases

