Cytoplasmic condensation is both necessary and sufficient to induce apoptotic cell death (VSports手机版)
- PMID: 18198188
- PMCID: "VSports最新版本" PMC2561226
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.017343
Cytoplasmic condensation is both necessary and sufficient to induce apoptotic cell death
Abstract
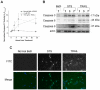
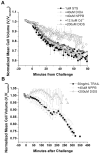
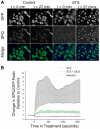
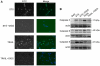
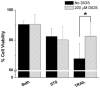
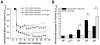
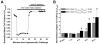
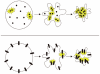
Programmed cell death (apoptosis) is important in tissue maintenance. Hallmarks of apoptosis include caspase activation, DNA fragmentation and an overall reduction in cell volume VSports手机版. Whether this apoptotic volume decrease (AVD) is a mere response to initiators of apoptosis or whether it is functionally significant is not clear. In this study, we sought to answer this question using human malignant glioma cells as a model system. In vivo, high grade gliomas demonstrate an increased percentage of apoptotic cells as well as upregulation of death ligand receptors. By dynamically monitoring cell volume, we show that the induction of apoptosis, via activation of either the intrinsic or extrinsic pathways with staurosporine or TRAIL, respectively, resulted in a rapid AVD in D54-MG human glioma cells. This decrease in cell volume could be prevented by inhibiting the efflux of Cl(-) through channels. Such suppression of AVD also reduced the activation of caspases 3, 8 and 9 and suppressed DNA fragmentation. Importantly, experimental manipulations that reduce the cell volume to 70% of the original volume for periods of at least 3 hours were sufficient to initiate apoptosis even in the absence of death ligands. Hence, this data suggests that cell condensation is both necessary and sufficient for the induction of apoptosis. .
Figures
"V体育平台登录" References
-
- Bortner CD, Cidlowski JA. Absence of volume regulatory mechanisms contributes to the rapid activation of apoptosis in thymocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 1996;271:C950–C961. - PubMed
-
- d’Anglemont de Tassigny A, Ghaleh B, Souktani R, Henry P, Berdeaux A. Hypo-osmotic stress inhibits doxorubicin-induced apoptosis via a protein kinase A-dependent mechanism in cardiomyocytes. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2004;31:438–443. - PubMed
-
- Fumarola C, Zerbini A, Guidotti GG. Glutamine deprivation-mediated cell shrinkage induces ligand-independent CD95 receptor signaling and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2001;8:1004–1013. - PubMed
Publication types
- VSports app下载 - Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Substances
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Grants and funding
VSports在线直播 - LinkOut - more resources
"VSports最新版本" Full Text Sources

