Rapamycin, but not cyclosporine or FK506, alters natural killer cell function (VSports最新版本)
- PMID: 18192925
- PMCID: "V体育官网入口" PMC4084728
- DOI: 10.1097/01.tp.0000296817.28053.7b (VSports手机版)
Rapamycin, but not cyclosporine or FK506, alters natural killer cell function
"VSports在线直播" Abstract
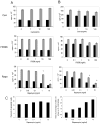
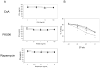
Infiltration of natural killer (NK) cells into solid organ allografts is observed in clinical and experimental transplantation. Studies suggest a role for NK cells in acute and chronic rejection of solid organ allografts; however, the effects of immunosuppressive agents on NK cells are not clearly established. Rat NK cell lines were analyzed for proliferation and cytotoxicity in the presence of cyclosporine, FK506, or rapamycin. Lewis recipients of DA liver allografts received immunosuppressive agents after transplantation VSports手机版. NK cells demonstrated robust function both in the absence and presence of cyclosporine and FK506. In contrast, rapamycin significantly inhibited proliferation and cytotoxicity of NK cells. NK cell numbers remained stable in graft recipients treated with cyclosporine and FK506, whereas there was a significant decrease in NK cells in rapamycin-treated recipients. These data indicate that immunosuppressive drugs have differential effects on NK cell function that may impact the immune response of transplant recipients. .
VSports最新版本 - Figures
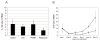
"V体育安卓版" References
-
- Ljunggren HG, Karre K. In search of the ‘missing self’: MHC molecules and NK cell recognition. Immunol Today. 1990;11:237. - PubMed
-
- Bottino C, Biassoni R, Millo R, et al. The human natural cytotoxicity receptors (NCR) that induce HLA class I-independent NK cell triggering. Hum Immunol. 2000;61:1. - PubMed
-
- Auchincloss H, Jr, Sachs DH. Xenogeneic transplantation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:433. - PubMed
-
- Blakely ML, Van der Werf WJ, Berndt MC, et al. Activation of intragraft endothelial and mononuclear cells during discordant xenograft rejection. Transplantation. 1994;58:1059. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (VSports手机版)
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
"VSports app下载" Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources (V体育2025版)
Full Text Sources
VSports app下载 - Other Literature Sources

