Immune recognition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mediated by the IPAF/NLRC4 inflammasome
- PMID: 18070936
- PMCID: PMC2150987
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20071239
Immune recognition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mediated by the IPAF/NLRC4 inflammasome
Abstract
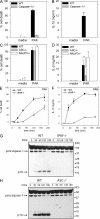
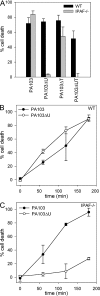
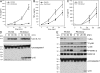
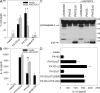
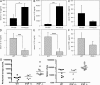
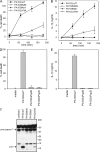
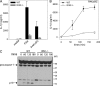
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative bacterium that causes opportunistic infections in immunocompromised individuals. P. aeruginosa employs a type III secretion system to inject effector molecules into the cytoplasm of the host cell. This interaction with the host cell leads to inflammatory responses that eventually result in cell death. We show that infection of macrophages with P. aeruginosa results in activation of caspase-1 in an IPAF-dependent, but flagellin-independent, manner. Macrophages deficient in IPAF or caspase-1 were markedly resistant to P. aeruginosa-induced cell death and release of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-1beta. A subset of P. aeruginosa isolates express the effector molecule exoenzyme U (ExoU), which we demonstrate is capable of inhibiting caspase-1-driven proinflammatory cytokine production VSports手机版. This study shows a key role for IPAF and capase-1 in innate immune responses to the pathogen P. aeruginosa, and also demonstrates that virulent ExoU-expressing strains of P. aeruginosa can circumvent this innate immune response. .
VSports最新版本 - Figures
References
-
- Barbieri, J.T., and J. Sun. 2004. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExoS and ExoT. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 152:79–92. - PubMed
-
- Sato, H., and D.W. Frank. 2004. ExoU is a potent intracellular phospholipase. Mol. Microbiol. 53:1279–1290. - PubMed
-
- He, S.Y., K. Nomura, and T.S. Whittam. 2004. Type III protein secretion mechanism in mammalian and plant pathogens. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1694:181–206. - PubMed
-
- Dacheux, D., J. Goure, J. Chabert, Y. Usson, and I. Attree. 2001. Pore-forming activity of type III system-secreted proteins leads to oncosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected macrophages. Mol. Microbiol. 40:76–85. - "VSports最新版本" PubMed
-
- Frithz-Lindsten, E., A. Holmström, L. Jacobsson, M. Soltani, J. Olsson, R. Rosqvist, and A. Forsberg. 1998. Functional conservation of the effector protein translocators PopB/YopB and PopD/YopD of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis.Mol. Microbiol. 29:1155–1165. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
V体育官网入口 - MeSH terms
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
Substances
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Grants and funding
"VSports" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports app下载" Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

