Genomic architecture and inheritance of human ribosomal RNA gene clusters
- PMID: 18025267
- PMCID: PMC2134781
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.6858507 (V体育2025版)
Genomic architecture and inheritance of human ribosomal RNA gene clusters
Abstract
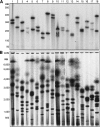
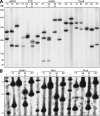
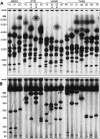
The finishing of the Human Genome Project largely completed the detailing of human euchromatic sequences; however, the most highly repetitive regions of the genome still could not be assembled. The 12 gene clusters producing the structural RNA components of the ribosome are critically important for cellular viability, yet fall into this unassembled region of the Human Genome Project. To determine the extent of human variation in ribosomal RNA gene content (rDNA) and patterns of rDNA cluster inheritance, we have determined the physical lengths of the rDNA clusters in peripheral blood white cells of healthy human volunteers. The cluster lengths exhibit striking variability between and within human individuals, ranging from 50 kb to >6 Mb, manifest essentially complete heterozygosity, and provide each person with their own unique rDNA electrophoretic karyotype. Analysis of these rDNA fingerprints in multigenerational human families demonstrates that the rDNA clusters are subject to meiotic rearrangement at a frequency >10% per cluster, per meiosis. With this high intrinsic recombinational instability, the rDNA clusters may serve as a unique paradigm of potential human genomic plasticity. VSports手机版.
Figures
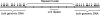
References
-
- Agresti A., Coull B.A., Coull B.A. Approximate is better than “exact” for interval estimation of binomial proportions. Am. Stat. 1998;2:119–125.
-
- Antonarakis S.E., Adelsberger P.A., Petersen M.B., Binkert F., Schinzel A.A., Adelsberger P.A., Petersen M.B., Binkert F., Schinzel A.A., Petersen M.B., Binkert F., Schinzel A.A., Binkert F., Schinzel A.A., Schinzel A.A. Analysis of DNA polymorphisms suggests that most de novo dup(21q) chromosomes in patients with Down syndrome are isochromosomes and not translocations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1990;47:968–972. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnheim N., Krystal M., Schmickel R., Wilson G., Ryder O., Zimmer E., Krystal M., Schmickel R., Wilson G., Ryder O., Zimmer E., Schmickel R., Wilson G., Ryder O., Zimmer E., Wilson G., Ryder O., Zimmer E., Ryder O., Zimmer E., Zimmer E. Molecular evidence for genetic exchanges among ribosomal genes on nonhomologous chromosomes in man and apes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1980;77:7323–7327. - V体育安卓版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birren B., Lai E., Lai E., editors. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis—A practical guide. Academic Press; San Diego, CA: 1993.
-
- Boyd L.J., Livingston J.S., Brown M.G., Lawce H.J., Gilhooly J.T., Wildin R.S., Linck L.M., Magenis R.E., Pillers D.A., Livingston J.S., Brown M.G., Lawce H.J., Gilhooly J.T., Wildin R.S., Linck L.M., Magenis R.E., Pillers D.A., Brown M.G., Lawce H.J., Gilhooly J.T., Wildin R.S., Linck L.M., Magenis R.E., Pillers D.A., Lawce H.J., Gilhooly J.T., Wildin R.S., Linck L.M., Magenis R.E., Pillers D.A., Gilhooly J.T., Wildin R.S., Linck L.M., Magenis R.E., Pillers D.A., Wildin R.S., Linck L.M., Magenis R.E., Pillers D.A., Linck L.M., Magenis R.E., Pillers D.A., Magenis R.E., Pillers D.A., Pillers D.A. Meiotic exchange event within the stalk region of an inverted chromosome 22 results in a recombinant chromosome with duplication of the distal long arm. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2005;138:355–360. - PubMed
"VSports app下载" Publication types
"VSports注册入口" MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
"V体育官网" Substances
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
