Inhibition of integrin alpha(v)beta6, an activator of latent transforming growth factor-beta, prevents radiation-induced lung fibrosis (VSports在线直播)
- PMID: 17916808
- PMCID: PMC2176115
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200706-806OC
V体育官网入口 - Inhibition of integrin alpha(v)beta6, an activator of latent transforming growth factor-beta, prevents radiation-induced lung fibrosis
"V体育官网入口" Abstract
Rationale: In experimental models, lung fibrosis is dependent on transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta signaling. TGF-beta is secreted in a latent complex with its propeptide, and TGF-beta activators release TGF-beta from this complex VSports手机版. Because the integrin alpha(v)beta6 is a major TGF-beta activator in the lung, inhibition of alpha(v)beta6-mediated TGF-beta activation is a logical strategy to treat lung fibrosis. .
Objectives: To determine, by genetic and pharmacologic approaches, whether murine radiation-induced lung fibrosis is dependent on alpha(v)beta6. V体育安卓版.
Methods: Wild-type mice, alpha(v)beta6-deficient (Itgb6-/-) mice, and mice heterozygous for a Tgfb1 mutation that eliminates integrin-mediated activation (Tgfb1(+/RGE)) were exposed to 14 Gy thoracic radiation. Some mice were treated with an anti-alpha(v)beta6 monoclonal antibody or a soluble TGF-beta receptor fusion protein. Alpha(v)beta6 expression was determined by immunohistochemistry. Fibrosis, inflammation, and gene expression patterns were assessed 20-32 weeks postirradiation V体育ios版. .
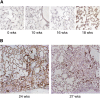
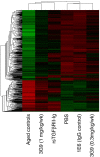
Measurements and main results: Beta6 integrin expression increased within the alveolar epithelium 18 weeks postirradiation, just before onset of fibrosis VSports最新版本. Itgb6-/- mice were completely protected from fibrosis, but not from late radiation-induced mortality. Anti-alpha(v)beta6 therapy (1-10 mg/kg/wk) prevented fibrosis, but only higher doses (6-10 mg/kg/wk) caused lung inflammation similar to that in Itgb6-/- mice. Tgfb1-haploinsufficient mice were also protected from fibrosis. .
Conclusions: Alpha(v)beta6-mediated TGF-beta activation is required for radiation-induced lung fibrosis V体育平台登录. Together with previous data, our results demonstrate a robust requirement for alpha(v)beta6 in distinct fibrosis models. Inhibition of alphavbeta6-mediated TGF-beta activation is a promising new approach for antifibrosis therapy. .
Figures
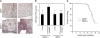

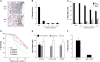

VSports - References
-
- Branton MH, Kopp JB. TGF-β and fibrosis. Microbes Infect 1999;1:1349–1365. - "V体育官网" PubMed
-
- Hyytiainen M, Penttinen C, Keski-Oja J. Latent TGF-β binding proteins: extracellular matrix association and roles in TGF-β activation. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 2004;41:233–264. - V体育官网 - PubMed
-
- Annes JP, Munger JS, Rifkin DB. Making sense of latent TGFβ activation. J Cell Sci 2003;116:217–224. - PubMed
"V体育安卓版" Publication types
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Substances
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
Grants and funding (VSports注册入口)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"V体育官网" Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

