"V体育ios版" Calmodulin-dependent kinase IV links Toll-like receptor 4 signaling with survival pathway of activated dendritic cells
- PMID: 17909078
- PMCID: "V体育平台登录" PMC2200860
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-05-091173
Calmodulin-dependent kinase IV links Toll-like receptor 4 signaling with survival pathway of activated dendritic cells
Abstract
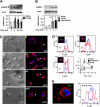
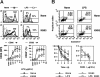
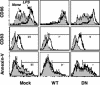
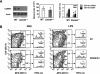
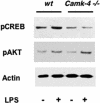
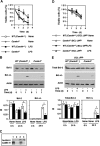
Microbial products, including lipopolysaccharide (LPS), an agonist of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), regulate the lifespan of dendritic cells (DCs) by largely undefined mechanisms VSports手机版. Here, we identify a role for calcium-calmodulin-dependent kinase IV (CaMKIV) in this survival program. The pharmacologic inhibition of CaMKs as well as ectopic expression of kinase-inactive CaMKIV decrease the viability of monocyte-derived DCs exposed to bacterial LPS. The defect in TLR4 signaling includes a failure to accumulate the phosphorylated form of the cAMP response element-binding protein (pCREB), Bcl-2, and Bcl-xL. CaMKIV null mice have a decreased number of DCs in lymphoid tissues and fail to accumulate mature DCs in spleen on in vivo exposure to LPS. Although isolated Camk4-/- DCs are able to acquire the phenotype typical of mature cells and release normal amounts of cytokines in response to LPS, they fail to accumulate pCREB, Bcl-2, and Bcl-xL and therefore do not survive. The transgenic expression of Bcl-2 in CaMKIV null mice results in full recovery of DC survival in response to LPS. These results reveal a novel link between TLR4 and a calcium-dependent signaling cascade comprising CaMKIV-CREB-Bcl-2 that is essential for DC survival. .
"VSports" Figures
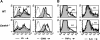
References
-
- Banchereau J, Steinman RM. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature. 1998;392:245–252. - PubMed
-
- Steinman RM. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:271–296. - PubMed
-
- Steinman RM, Bonifaz L, Fujii S, et al. The innate functions of dendritic cells in peripheral lymphoid tissues. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2005;560:83–97. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育安卓版)
"VSports app下载" Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

