An IgG-like domain in the minor pilin GBS52 of Streptococcus agalactiae mediates lung epithelial cell adhesion
- PMID: 17697995
- PMCID: PMC2844079
- DOI: "VSports手机版" 10.1016/j.str.2007.06.015
VSports app下载 - An IgG-like domain in the minor pilin GBS52 of Streptococcus agalactiae mediates lung epithelial cell adhesion
Abstract
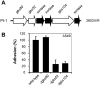
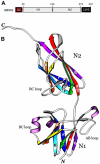
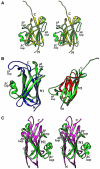
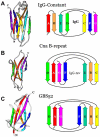
Streptococcus agalactiae is the leading cause of neonatal pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis VSports手机版. The pathogen assembles heterotrimeric pilus structures on its surface; however, their function in pathogenesis is poorly understood. We report here the crystal structure of the pilin GBS52, which reveals two IgG-like fold domains, N1 and N2. Each domain is comprised of seven antiparallel beta strands, an arrangement similar to the fold observed in the Staphylococcus aureus adhesin Cna. Consistent with its role as an adhesin, deletion of gbs52 gene significantly reduces bacterial adherence to pulmonary epithelial cells. Moreover, latex beads linked to the GBS52 protein adhere to pulmonary but not to many other epithelial cells; binding to the former is specifically inhibited by antibodies against GBS52. Nonetheless, substantial binding is only observed with N2 domain-conjugated beads. This study presents the structure of a Gram-positive pilin that utilizes a distinct IgG fold variant to mediate pathogen adherence to a specific tissue. .
Figures
References
-
- Baker C, Edward M. Group B streptococcal infections. In: Remington JS, Klein JO, editors. Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant. W.B. Saunders; Philadelphia: 2001. pp. 1091–1156.
-
- Barocchi MA, Ries J, Zogaj X, Hemsley C, Albiger B, Kanth A, Dahlberg S, Fernebro J, Moschioni M, Masignani V, et al. A pneumococcal pilus influences virulence and host inflammatory responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2006;103:2857–2862. - V体育ios版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brunger AT, Adams PD, Clore GM, DeLano WL, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Jiang JS, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu NS, et al. Crystallography & NMR System: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1998;54:905–921. - PubMed
-
- CCP4 (Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4) The CCP4 suites: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1994;50:760–763. - PubMed
-
- Cieslewicz MJ, Kasper DL, Wang Y, Wessels MR. Functional analysis in type Ia group B Streptococcus of a cluster of genes involved in extracellular polysaccharide production by diverse species of streptococci. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:139–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
VSports在线直播 - Substances
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
Associated data (VSports注册入口)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育2025版)
Other Literature Sources

