"V体育安卓版" Branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: observations in 145 patients who underwent resection
- PMID: 17631133
- PMCID: PMC3807096
- DOI: "VSports" 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.05.010
Branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: observations in 145 patients who underwent resection
Abstract
Background & aims: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) of the pancreas arising in branch ducts are thought to be less aggressive than their main-duct counterparts, and guidelines for their conservative management were recently proposed VSports手机版. This study describes the combined experience of 2 tertiary centers with branch-duct IPMNs aiming to validate these recommendations. .
Methods: A review of 145 patients with resected, pathologically confirmed, branch-duct IPMNs between 1990 and 2005 was conducted. V体育安卓版.
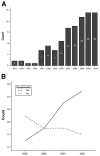
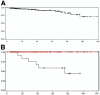
Results: Sixty-six patients (45. 5%) had adenoma, 47 (32%) borderline tumors, 16 (11%) carcinoma in situ, and 16 (11%) invasive carcinoma. Median age was similar between benign and malignant subgroups (66 vs 67. 5 years, respectively). Jaundice was more frequent in patients with cancer (12. 5% vs 1. 8%, respectively, P = . 022) and abdominal pain in patients with benign tumors (45% vs 25%, respectively, P = . 025). Forty percent of tumors were discovered incidentally. Findings associated with malignancy were the presence of a thick wall (P < V体育ios版. 001), nodules (P < . 001), and tumor diameter >or=30 mm (P < . 001). All neoplasms with cancer were larger than 30 mm in size or had nodules or caused symptoms. After a mean follow-up of 45 months, the 5-year disease-specific survival for branch-duct IPMNs with noninvasive neoplasms was 100% and, for invasive cancer, was 63%. .
Conclusions: This large cohort of resected branch-duct IPMNs shows that cancer is present in 22% of cases and validates the recent guidelines that indicate absence of malignancy in tumors <30 mm, without symptoms or mural nodules. VSports最新版本.
Figures

VSports手机版 - Comment in
-
Location, location, location: precursors and prognoses for pancreatic cancer.Gastroenterology. 2007 Jul;133(1):345-50. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.05.059. Gastroenterology. 2007. PMID: 17631154 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sohn TA, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Hruban RH, Fukushima N, Campbell KA, Lillemoe KD. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: an updated experience. Ann Surg. 2004;239:788–799. - "VSports" PMC - PubMed
-
- Conlon KC. Intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:4518–4523. - PubMed
-
- Traverso LW, Peralta EA, Ryan JA, Jr, Kozarek RA. Intraductal neoplasms of the pancreas. Am J Surg. 1998;175:426–432. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
MeSH terms
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
"V体育安卓版" Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
V体育ios版 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"V体育官网" Medical

