Manipulation of the toll-like receptor 7 signaling pathway by Epstein-Barr virus
- PMID: 17609264
- PMCID: PMC2045431
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01122-07
V体育官网入口 - Manipulation of the toll-like receptor 7 signaling pathway by Epstein-Barr virus
"V体育安卓版" Abstract
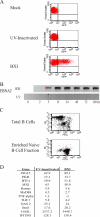
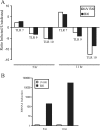
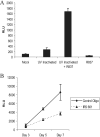
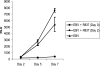
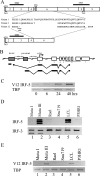
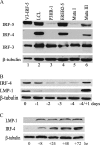
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection of primary B cells causes B-cell activation and proliferation. Activation of B cells requires binding of antigen to the B-cell receptor and a survival signal from ligand-bound CD40, signals that are provided by the EBV LMP1 and LMP2A latency proteins. Recently, Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling has been reported to provide a third B-cell activation stimulus VSports手机版. The interaction between the EBV and TLR pathways was therefore investigated. Both UV-inactivated and untreated EBV upregulated the expression of TLR7 and downregulated the expression of TLR9 in naive B cells. UV-inactivated virus transiently stimulated naive B-cell proliferation in the presence of the TLR7 ligand R837, while addition of the TLR7 antagonist IRS 661 impaired cell growth induced by untreated EBV. Interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF-5) is a downstream mediator of TLR7 signaling. IRF-5 was induced following EBV infection, and IRF-5 was expressed in B-cell lines with type III latency. Expression of IRF-5 in this setting is surprising since IRF-5 has tumor suppressor and antiviral properties. B-cell proliferation assays provided evidence that EBV modulates TLR7 signaling responses. Examination of IRF-5 transcripts identified a novel splice variant, V12, that was induced by EBV infection, was constitutively nuclear, and acted as a dominant negative form in IRF-5 reporter assays. IRF-4 negatively regulates IRF-5 activation, and IRF-4 was also present in type III latently infected cells. EBV therefore initially uses TLR7 signaling to enhance B-cell proliferation and subsequently modifies the pathway to regulate IRF-5 activity. .
Figures
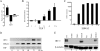

References
-
- Akira, S., and K. Takeda. 2004. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:499-511. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, B. J., M. J. Kellum, K. E. Pinder, J. A. Frisancho, and P. M. Pitha. 2003. Interferon regulatory factor 5, a novel mediator of cell cycle arrest and cell death. Cancer Res. 63:6424-6431. - "V体育ios版" PubMed
-
- Barnes, B. J., P. A. Moore, and P. M. Pitha. 2001. Virus-specific activation of a novel interferon regulatory factor, IRF-5, results in the induction of distinct interferon alpha genes. J. Biol. Chem. 276:23382-23390. - PubMed (VSports app下载)
Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Substances
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
VSports - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
VSports手机版 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"V体育ios版" Research Materials

