A top-down systems biology view of microbiome-mammalian metabolic interactions in a mouse model
- PMID: 17515922
- PMCID: PMC2673711
- DOI: 10.1038/msb4100153
"V体育官网入口" A top-down systems biology view of microbiome-mammalian metabolic interactions in a mouse model
Abstract
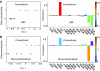
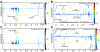
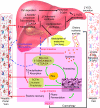
Symbiotic gut microorganisms (microbiome) interact closely with the mammalian host's metabolism and are important determinants of human health. Here, we decipher the complex metabolic effects of microbial manipulation, by comparing germfree mice colonized by a human baby flora (HBF) or a normal flora to conventional mice. We perform parallel microbiological profiling, metabolic profiling by (1)H nuclear magnetic resonance of liver, plasma, urine and ileal flushes, and targeted profiling of bile acids by ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and short-chain fatty acids in cecum by GC-FID. Top-down multivariate analysis of metabolic profiles reveals a significant association of specific metabotypes with the resident microbiome. We derive a transgenomic graph model showing that HBF flora has a remarkably simple microbiome/metabolome correlation network, impacting directly on the host's ability to metabolize lipids: HBF mice present higher ileal concentrations of tauro-conjugated bile acids, reduced plasma levels of lipoproteins but higher hepatic triglyceride content associated with depletion of glutathione VSports手机版. These data indicate that the microbiome modulates absorption, storage and the energy harvest from the diet at the systems level. .
"V体育官网入口" Figures

Comment in (V体育官网入口)
-
Top-down versus bottom-up-rediscovering physiology via systems biology?Mol Syst Biol. 2007;3:113. doi: 10.1038/msb4100154. Epub 2007 May 22. Mol Syst Biol. 2007. PMID: 17515923 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Armstrong MJ, Carey MC (1982) The hydrophobic–hydrophilic balance of bile salts. Inverse correlation between reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatographic mobilities and micellar cholesterol-solubilizing capacities. J Lipid Res 23: 70–80 - PubMed
-
- Backhed F, Ley R, Sonnenburg J, Peterson D, Gordon J (2005) Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 307: 1915–1920 - PubMed
-
- Bax A, Davis D (1985) MLEV-17-based two-dimensional homonuclear magnetization transfer spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 65: 355–360
-
- Bollard ME, Keun HC, Beckonert O, Ebbels TM, Antti H, Nicholls AW, Shockcor JP, Cantor GH, Stevens G, Lindon JC, Holmes E, Nicholson JK (2005) Comparative metabonomics of differential hydrazine toxicity in the rat and mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 204: 135–151 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育官网" Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

