Chromatin remodeling by the SWI/SNF-like BAF complex and STAT4 activation synergistically induce IL-12Rbeta2 expression during human Th1 cell differentiation
- PMID: 17304212
- PMCID: PMC1817634
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601586
"V体育官网入口" Chromatin remodeling by the SWI/SNF-like BAF complex and STAT4 activation synergistically induce IL-12Rbeta2 expression during human Th1 cell differentiation
Abstract
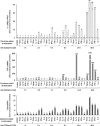
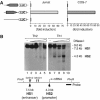
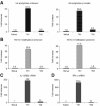
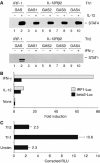
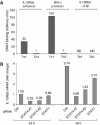
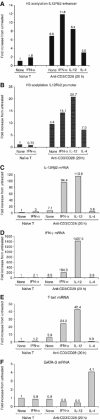
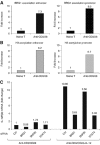
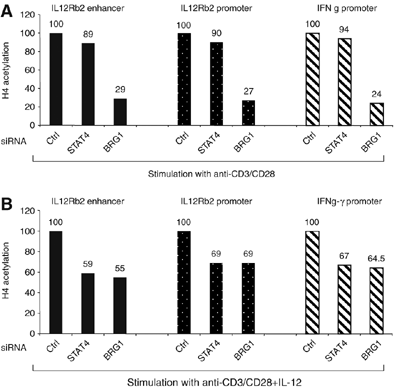
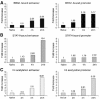
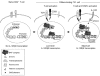
Interleukin-12 (IL-12) is a key cytokine for the development of T helper type 1 (Th1) responses; however, naïve CD4(+) T cells do not express IL-12Rbeta2, and are therefore unresponsive to IL-12. We have examined the mechanisms that control Th1-specific expression of the human IL-12Rbeta2 gene at early time points after T-cell stimulation VSports手机版. We have identified a Th1-specific enhancer element that binds signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (STAT4) in vivo in developing Th1 but not Th2 cells. T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling induced histone hyperacetylation and recruitment of BRG1, the ATPase subunit of the SWI/SNF-like BAF chromatin remodeling complex, to the IL-12Rbeta2 regulatory regions and was associated with low-level gene transcription at the IL-12Rbeta2 locus. However, high-level IL-12Rbeta2 expression required TCR triggering in the presence of IL-12. Our results indicate a synergistic role of TCR-induced chromatin remodeling and cytokine-induced STAT4 activation to direct IL-12Rbeta2 expression during Th1 cell development. .
VSports手机版 - Figures
References
-
- Afkarian M, Sedy JR, Yang J, Jacobson NG, Cereb N, Yang SY, Murphy TL, Murphy KM (2002) T-bet is a STAT1-induced regulator of IL-12R expression in naive CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol 3: 549–557 - PubMed
-
- Agarwal S, Rao A (1998) Modulation of chromatin structure regulates cytokine gene expression during T cell differentiation. Immunity 9: 765–775 - PubMed
-
- Ansel KM, Lee DU, Rao A (2003) An epigenetic view of helper T cell differentiation. Nat Immunol 4: 616–623 - PubMed
-
- Athie-Morales V, Smits HH, Cantrell DA, Hilkens CM (2004) Sustained IL-12 signaling is required for Th1 development. J Immunol 172: 61–69 - PubMed
-
- Avni O, Lee D, Macian F, Szabo SJ, Glimcher LH, Rao A (2002) T(H) cell differentiation is accompanied by dynamic changes in histone acetylation of cytokine genes. Nat Immunol 3: 643–651 - PubMed (V体育2025版)
VSports - Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
Substances
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
"VSports最新版本" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

