V体育官网 - CD34+ hematopoietic stem-progenitor cell microRNA expression and function: a circuit diagram of differentiation control
- PMID: 17293455
- PMCID: PMC1796783
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0610983104
CD34+ hematopoietic stem-progenitor cell microRNA expression and function: a circuit diagram of differentiation control
Abstract
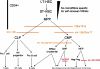
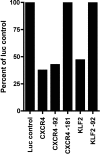
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a recently identified class of epigenetic elements consisting of small noncoding RNAs that bind to the 3' untranslated region of mRNAs and down-regulate their translation to protein. miRNAs play critical roles in many different cellular processes including metabolism, apoptosis, differentiation, and development. We found 33 miRNAs expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic stem-progenitor cells (HSPCs) from normal human bone marrow and mobilized human peripheral blood stem cell harvests. We then combined these data with human HSPC mRNA expression data and with miRNA-mRNA target predictions, into a previously undescribed miRNA:mRNA interaction database called the Transcriptome Interaction Database. The in silico predictions from the Transcriptome Interaction Database pointed to miRNA control of hematopoietic differentiation through translational control of mRNAs critical to hematopoiesis. From these predictions, we formulated a model for miRNA control of stages of hematopoiesis in which many of the genes specifying hematopoietic differentiation are expressed by HSPCs, but are held in check by miRNAs until differentiation occurs. We validated miRNA control of several of these target mRNAs by demonstrating that their translation in fact is decreased by miRNAs. Finally, we chose miRNA-155 for functional characterization in hematopoiesis, because we predicted that it would control both myelopoiesis and erythropoiesis VSports手机版. As predicted, miRNA-155 transduction greatly reduced both myeloid and erythroid colony formation of normal human HSPCs. .
Conflict of interest statement (VSports注册入口)
Conflict of interest statement: The Johns Hopkins University holds patents on CD34 monoclonal antibodies and inventions related to stem cells. C. I. C. is entitled to a share of the sales royalty received by the university under licensing agreements between the university, Becton Dickinson Corp V体育安卓版. , and Baxter HealthCare Corp. The terms of this arrangement are being managed by The Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict of interest policies.
Figures (VSports注册入口)


References
-
- Finnegan EJ, Matzke MA. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:4689–4693. - "V体育安卓版" PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF, Bartel DP. Science. 2004;303:83–86. - PubMed
-
- Felli N, Fontana L, Pelosi E, Botta R, Bonci D, Facchiano F, Liuzzi F, Lulli V, Morsilli O, Santoro S, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:18081–18086. - "V体育ios版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Fazi F, Rosa A, Fatica A, Gelmetti V, De Marchis ML, Nervi C, Bozzoni I. Cell. 2005;123:819–831. - PubMed
"VSports最新版本" Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports)
Grants and funding
"VSports最新版本" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (VSports)
Medical
VSports在线直播 - Research Materials

