Submicromolar concentrations of 4-hydroxynonenal induce glutamate cysteine ligase expression in HBE1 cells
- PMID: 17263920
- PMCID: V体育官网入口 - PMC2730489
- DOI: 10.1179/135100007X162266
Submicromolar concentrations of 4-hydroxynonenal induce glutamate cysteine ligase expression in HBE1 cells
VSports - Abstract
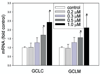
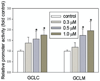
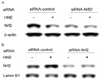
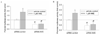
4-Hydroxynonenal (HNE), a major electrophilic product of lipid peroxidation, is regarded as both a marker of oxidative stress and a mediator of oxidative damage. At subtoxic concentrations, however, this compound has been shown to be a signalling molecule that can induce the expression of various antioxidant/detoxification enzymes, including glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL), the rate-limiting enzyme in the de novo synthesis of glutathione. GCL consists of a catalytic (GCLC) and modulatory (GCLM) subunit, which are encoded by separate genes VSports手机版. Here, we investigated the effect of submicromolar concentrations of HNE on the expression of the GCL genes and the transcription factors involved. We demonstrated that submicromolar concentrations of HNE (as little as 0. 3 muM) could increase the expression of both GCLC and GCLM. We also found that the induction of GCL expression was abrogated by siRNA for Nrf2. Our data suggest that a submicromolar concentration of HNE, as found in human plasma under physiological conditions, can induce GCL transcription in cultured cells implying that 'basal' expression of GCL is under regulation by lipid peroxidation that occurs under physiological conditions. Moreover, this induction is mediated through the EpRE-Nrf2 signalling pathway thought to be predominantly active only during stress. .
VSports手机版 - Figures
"VSports在线直播" References
-
- Esterbauer H, Schaur RJ, Zollner H. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic Biol Med. 1991;11:81–128. - PubMed
-
- Uchida K. 4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal: a product and mediator of oxidative stress. Prog Lipid Res. 2003;42:318–343. - PubMed
-
- Leonarduzzi G, Robbesyn F, Poli G. Signaling kinases modulated by 4-hydroxynonenal. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004;37:1694–1702. - PubMed
-
- Cambiaggi C, Dominici S, Comporti M, Pompella A. Modulation of human T lymphocyte proliferation by 4-hydroxynonenal, the bioactive product of neutrophil-dependent lipid peroxidation. Life Sci. 1997;61:777–785. - PubMed
-
- Awasthi YC, Yang Y, Tiwari NK, et al. Regulation of 4-hydroxynonenal-mediated signaling by glutathione S-transferases. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004;37:607–619. - PubMed
Publication types (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
MeSH terms
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
Substances
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials (V体育官网)
Miscellaneous
