"V体育官网" Combinatorial pattern recognition receptor signaling alters the balance of life and death in macrophages
- PMID: 17167049
- PMCID: PMC1750881
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0609671104
Combinatorial pattern recognition receptor signaling alters the balance of life and death in macrophages
Abstract
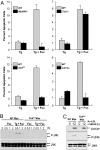
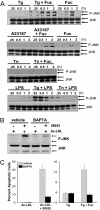
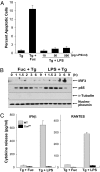
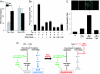
Macrophage pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) play key roles in innate immunity, but they also may contribute to disease processes under certain pathological conditions. We recently showed that engagement of the type A scavenger receptor (SRA), a PRR, triggers JNK-dependent apoptosis in endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-stressed macrophages VSports手机版. In advanced atherosclerotic lesions, the SRA, activated JNK, and ER stress are observed in macrophages, and macrophage death in advanced atheromata leads to plaque necrosis. Herein, we show that SRA ligands trigger apoptosis in ER-stressed macrophages by cooperating with another PRR, Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), to redirect TLR4 signaling from prosurvival to proapoptotic. Common SRA ligands activate both TLR4 signaling and engage the SRA. The TLR4 effect results in activation of the proapoptotic MyD88-JNK branch of TLR4, whereas the SRA effect silences the prosurvival IRF-3-IFN-beta branch of TLR4. The normal cell-survival effect of LPS-induced TLR4 activation is converted into an apoptosis response by immunoneutralization of IFN-beta, and the apoptosis effect of SRA ligands is converted into a cell-survival response by reconstitution with IFN-beta. Thus, combinatorial signaling between two distinct PRRs results in a functional outcome-macrophage apoptosis that does not occur with either PRR alone. PRR-induced macrophage death may play important roles in advanced atherosclerosis and in other innate immunity-related processes in which the balance between macrophage survival and death is critical. .
"VSports在线直播" Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Glass CK, Witztum JL. Cell. 2001;104:503–516. - PubMed (VSports)
-
- Tabas I. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:2255–2264. - "VSports手机版" PubMed
-
- Ball RY, Stowers EC, Burton JH, Cary NR, Skepper JN, Mitchinson MJ. Atherosclerosis. 1995;114:45–54. - PubMed
-
- Libby P, Geng YJ, Aikawa M, Schoenbeck U, Mach F, Clinton SK, Sukhova GK, Lee RT. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1996;7:330–335. - PubMed
VSports - Publication types
- "VSports app下载" Actions
"VSports注册入口" MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Substances
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
Grants and funding (VSports在线直播)
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports最新版本" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (VSports)
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

