Insulin regulation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase expression in human hepatocytes: roles of forkhead box O1 and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c
- PMID: 16885156
- PMCID: PMC1576296
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M605815200
Insulin regulation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase expression in human hepatocytes: roles of forkhead box O1 and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c
"VSports最新版本" Abstract
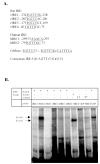
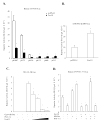
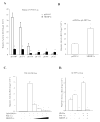
Bile acid synthesis and pool size increases in diabetes, whereas insulin inhibits bile acid synthesis. The objective of this study is to elucidate the mechanism of insulin regulation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene expression in human hepatocytes. Real-time PCR assays showed that physiological concentrations of insulin rapidly stimulated cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) mRNA expression in primary human hepatocytes but inhibited CYP7A1 expression after extended treatment. The insulin-regulated forkhead box O1 (FoxO1) and steroid regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) strongly inhibited hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha trans-activation of the CYP7A1 gene. FoxO1 binds to an insulin response element in the rat CYP7A1 promoter, which is not present in the human CYP7A1 gene. Insulin rapidly phosphorylates and inactivates FoxO1, whereas insulin induces nuclear SREBP-1c expression in human primary hepatocytes. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay shows that insulin reduced FoxO1 and peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor gamma-coactivator-1alpha but increased SREBP-1c recruitment to CYP7A1 chromatin. We conclude that insulin has dual effects on human CYP7A1 gene transcription; physiological concentrations of insulin rapidly inhibit FoxO1 activity leading to stimulation of the human CYP7A1 gene, whereas prolonged insulin treatment induces SREBP-1c, which inhibits human CYP7A1 gene transcription. Insulin may play a major role in the regulation of bile acid synthesis and dyslipidemia in diabetes VSports手机版. .
Figures




References
-
- Reaven G, Abbasi F, McLaughlin T. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2004;59:207–223. - PubMed
-
- Chiang JYL. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003;284:G349–G356. - PubMed
-
- Bennion LJ, Grundy SM. N Engl J Med. 1977;296:1365–1371. - PubMed (VSports手机版)
-
- Andersen E, Karlaganis G, Sjovall J. Eur J Clin Inv. 1988;18:166–172. - PubMed
-
- Hassan AS, Ravi Subbiah MT, Thiebert P. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980;164:449–452. - "VSports手机版" PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (VSports手机版)
"V体育官网" MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
"VSports手机版" Substances
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
"V体育2025版" Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

