"V体育2025版" Regulation of hepatic fatty acid elongase and desaturase expression in diabetes and obesity
- PMID: 16790840
- PMCID: PMC2764365 (V体育官网)
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M600177-JLR200
V体育安卓版 - Regulation of hepatic fatty acid elongase and desaturase expression in diabetes and obesity
"VSports" Erratum in
- J Lipid Res. 2006 Oct;47(10):2353. Nair, Muraleedharan [corrected to Nair, Muraleedharan G]; Peters, Jeffery M [corrected to Peters, Jeffrey M]; Busik, Julia [corrected to Busik, Julia V]
"VSports" Abstract
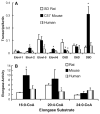
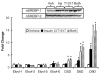
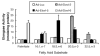
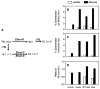
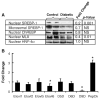
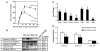
Fatty acid elongases and desaturases play an important role in hepatic and whole body lipid composition. We examined the role that key transcription factors played in the control of hepatic elongase and desaturase expression. Studies with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha)-deficient mice establish that PPARalpha was required for WY14643-mediated induction of fatty acid elongase-5 (Elovl-5), Elovl-6, and all three desaturases [Delta(5) desaturase (Delta(5)D), Delta(6)D, and Delta(9)D]. Increased nuclear sterol-regulatory element binding protein-1 (SREBP-1) correlated with enhanced expression of Elovl-6, Delta(5)D, Delta(6)D, and Delta(9)D. Only Delta(9)D was also regulated independently by liver X receptor (LXR) agonist. Glucose induction of l-type pyruvate kinase, Delta(9)D, and Elovl-6 expression required the carbohydrate-regulatory element binding protein/MAX-like factor X (ChREBP/MLX) heterodimer. Suppression of Elovl-6 and Delta(9)D expression in livers of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats and high fat-fed glucose-intolerant mice correlated with low levels of nuclear SREBP-1 VSports手机版. In leptin-deficient obese mice (Lep(ob/ob)), increased SREBP-1 and MLX nuclear content correlated with the induction of Elovl-5, Elovl-6, and Delta(9)D expression and the massive accumulation of monounsaturated fatty acids (18:1,n-7 and 18:1,n-9) in neutral lipids. Diabetes- and obesity-induced changes in hepatic lipid composition correlated with changes in elongase and desaturase expression. In conclusion, these studies establish a role for PPARalpha, LXR, SREBP-1, ChREBP, and MLX in the control of hepatic fatty acid elongase and desaturase expression and lipid composition. .
Figures
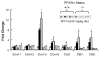
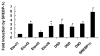

References
-
- Jump DB, Clarke SD. Regulation of gene expression by dietary fat. Annu Rev Nutr. 1999;19:63–90. - PubMed
-
- Jump DB. Fatty acid regulation of gene transcription. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2004;41:41–78. - "V体育官网" PubMed
-
- Hillgartner FB, Salati LM, Goodridge AG. Physiological and molecular mechanisms involved in nutritional regulation of fatty acid synthesis. Physiol Rev. 1995;75:47–76. - PubMed
-
- Sprecher H. Metabolism of highly unsaturated n-3 and n-6 fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1486:219–231. - PubMed
-
- Pawar A, Xu J, Jerks E, Mangelsdorf DJ, Jump DB. Fatty acid regulation of liver X receptors (LXR) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in HEK293 cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:39243–39250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
"V体育安卓版" Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
VSports - Miscellaneous

