"V体育安卓版" Characterization of RNase R-digested cellular RNA source that consists of lariat and circular RNAs from pre-mRNA splicing
- PMID: 16682442
- PMCID: VSports在线直播 - PMC1458517
- DOI: "V体育平台登录" 10.1093/nar/gkl151
Characterization of RNase R-digested cellular RNA source that consists of lariat and circular RNAs from pre-mRNA splicing
Abstract
Besides linear RNAs, pre-mRNA splicing generates three forms of RNAs: lariat introns, Y-structure introns from trans-splicing, and circular exons through exon skipping. To study the persistence of excised introns in total cellular RNA, we used three Escherichia coli 3' to 5' exoribonucleases. Ribonuclease R (RNase R) thoroughly degrades the abundant linear RNAs and the Y-structure RNA, while preserving the loop portion of a lariat RNA VSports手机版. Ribonuclease II (RNase II) and polynucleotide phosphorylase (PNPase) also preserve the lariat loop, but are less efficient in degrading linear RNAs. RNase R digestion of the total RNA from human skeletal muscle generates an RNA pool consisting of lariat and circular RNAs. RT-PCR across the branch sites confirmed lariat RNAs and circular RNAs in the pool generated by constitutive and alternative splicing of the dystrophin pre-mRNA. Our results indicate that RNase R treatment can be used to construct an intronic cDNA library, in which majority of the intron lariats are represented. The highly specific activity of RNase R implies its ability to screen for rare intragenic trans-splicing in any target gene with a large background of cis-splicing. Further analysis of the intronic RNA pool from a specific tissue or cell will provide insights into the global profile of alternative splicing. .
VSports app下载 - Figures

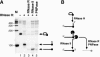

References
-
- International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - VSports - PubMed
-
- International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium. Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome. Nature. 2004;431:931–945. - PubMed
-
- Venter J.C., Adams M.D., Myers E.W., Li P.W., Mural R.J., Sutton G.G., Smith H.O., Yandell M., Evans C.A., Holt R.A., et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science. 2001;291:1304–1351. - PubMed
-
- Hayashizaki Y., Kanamori M. Dynamic transcriptome of mice. Trends Biotechnol. 2004;22:161–167. - PubMed
-
- Harbers M., Carninci P. Tag-based approaches for transcriptome research and genome annotation. Nature Methods. 2005;2:495–502. - "VSports最新版本" PubMed
"VSports在线直播" Publication types
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (V体育官网)
Substances
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
VSports app下载 - Other Literature Sources
Medical

