Structure of human Wilson protein domains 5 and 6 and their interplay with domain 4 and the copper chaperone HAH1 in copper uptake
- PMID: 16571664
- PMCID: "V体育ios版" PMC1458641
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0504472103
Structure of human Wilson protein domains 5 and 6 and their interplay with domain 4 and the copper chaperone HAH1 in copper uptake
Abstract
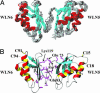
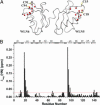
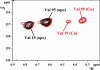
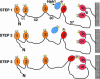
Human Wilson protein is a copper-transporting ATPase located in the secretory pathway possessing six N-terminal metal-binding domains. Here we focus on the function of the metal-binding domains closest to the vesicular portion of the copper pump, i. e. , domain 4 (WLN4), and a construct of domains 5 and 6 (WLN5-6). For comparison purposes, some experiments were also performed with domain 2 (WLN2) VSports手机版. The solution structure of apoWLN5-6 consists of two ferredoxin folds connected by a short linker, and (15)N relaxation rate measurements show that it behaves as a unit in solution. An NMR titration of apoWLN5-6 with the metallochaperone Cu(I)HAH1 reveals no complex formation and no copper exchange between the two proteins, whereas titration of Cu(I)HAH1 with WLN4 shows the formation of an adduct that is in fast exchange on the NMR time scale with the isolated protein species as confirmed by (15)N relaxation data. A similar interaction is also observed between Cu(I)HAH1 and WLN2; however, the relative amount of the adduct in the protein mixture is lower. An NMR titration of apoWLN5-6 with Cu(I)WLN4 shows copper transfer, first to WLN6 then to WLN5, without the formation of an adduct. Therefore, we suggest that WLN4 and WLN2 are two acceptors of Cu(I) from HAH1, which then somehow route copper to WLN5-6, before the ATP-driven transport of copper across the vesicular membrane. .
VSports app下载 - Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
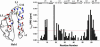
References
-
- Tanzi R. E., Petrukhin K., Chernov I., Pellequer J. L., Wasco W., Ross B., Romano D. M., Parano E., Pavone L., Brzustowicz L. M., et al. Nat. Genet. 1993;5:344–350. - PubMed
-
- Bull P. C., Thomas G. R., Rommens J. M., Forbes J. R., Cox D. W. Nat. Genet. 1993;5:327–337. - PubMed (VSports最新版本)
-
- Lutsenko S., Petris M. J. J. Membr. Biol. 2003;191:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Thomas G. R., Forbes J. R., Roberts E. A., Walshe J. M., Cox D. W. Nat. Genet. 1995;9:210–217. - VSports手机版 - PubMed
-
- Mercer J. F. Trends Mol. Med. 2001;7:64–69. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (VSports)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育官网" Actions
Substances
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Associated data
"VSports app下载" Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
V体育官网入口 - Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous (VSports手机版)

