Transmission of nephridial bacteria of the earthworm Eisenia fetida
- PMID: 16391117
- PMCID: PMC1352274
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.72.1.769-775.2006
Transmission of nephridial bacteria of the earthworm Eisenia fetida (V体育官网入口)
"VSports在线直播" Abstract
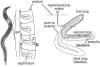
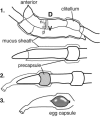
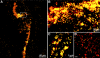
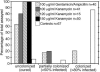
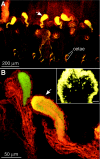
The lumbricid earthworms (annelid family Lumbricidae) harbor gram-negative bacteria in their excretory organs, the nephridia. Comparative 16S rRNA gene sequencing of bacteria associated with the nephridia of several earthworm species has shown that each species of worm harbors a distinct bacterial species and that the bacteria from different species form a monophyletic cluster within the genus Acidovorax, suggesting that there is a specific association resulting from radiation from a common bacterial ancestor. Previous microscopy and culture studies revealed the presence of bacteria within the egg capsules and on the surface of embryos but did not demonstrate that the bacteria within the egg capsule were the same bacteria that colonized the nephridia. We present evidence, based on curing experiments, in situ hybridizations with Acidovorax-specific probes, and 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, that the egg capsules contain high numbers of the bacterial symbiont and that juveniles are colonized during development within the egg capsule VSports手机版. Studies exposing aposymbiotic hatchlings to colonized adults and their bedding material suggested that juvenile earthworms do not readily acquire bacteria from the soil after hatching but must be colonized during development by bacteria deposited in the egg capsule. Whether this is due to the developmental stage of the host or the physiological state of the symbiont remains to be investigated. .
Figures

References
-
- Alves, A., O. Santos, I. Henriques, and A. Correia. 2002. Evaluation of methods for molecular typing and identification of members of the genus Brevibacterium and other related species. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 213:205-211. - PubMed
-
- Baumann, P., N. A. Moran, and L. Baumann. 2000. Bacteriocyte-associated endosymbionts of insects. In M. Dworkin (ed.), The prokaryotes, a handbook on the biology of bacteria: ecophysiology, isolation, identification, applications, 3rd ed. [Online.] Springer-Verlag, New York, N.Y. http://141.150.157.117:8080/prokPUB/chaprender/jsp/showchap.jsp?chapnum=243.
-
- Bright, M., and O. Giere. 2005. Microbial symbiosis in Annelida. Symbiosis 38:1-45.
-
- Brown, B. A., and M. J. Mitchell. 1981. Role of the earthworm, Eisenia fetida, in affecting survival of Salmonella enteritidis ser. Typhimurium. Pedobiologia 22:434-438.
Publication types (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
MeSH terms
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Substances
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
Associated data
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

