"VSports在线直播" Embryonic stem cell-derived hematopoietic stem cells
- PMID: 16357205
- PMCID: "V体育平台登录" PMC1323159
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0506127102
Embryonic stem cell-derived hematopoietic stem cells
Erratum in
-
Correction for Wang et al., Embryonic stem cell-derived hematopoietic stem cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Aug 3;118(31):e2112407118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2112407118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34312242 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
"V体育ios版" Abstract
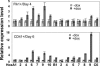
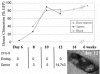
Despite two decades of studies documenting the in vitro blood-forming potential of murine embryonic stem cells (ESCs), achieving stable long-term blood engraftment of ESC-derived hematopoietic stem cells in irradiated mice has proven difficult. We have exploited the Cdx-Hox pathway, a genetic program important for blood development, to enhance the differentiation of ESCs along the hematopoietic lineage. Using an embryonic stem cell line engineered with tetracycline-inducible Cdx4, we demonstrate that ectopic Cdx4 expression promotes hematopoietic mesoderm specification, increases hematopoietic progenitor formation, and, together with HoxB4, enhances multilineage hematopoietic engraftment of lethally irradiated adult mice. Clonal analysis of retroviral integration sites confirms a common stem cell origin of lymphoid and myeloid populations in engrafted primary and secondary mice VSports手机版. These data document the cardinal stem cell features of self-renewal and multilineage differentiation of ESC-derived hematopoietic stem cells. .
VSports注册入口 - Figures

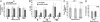
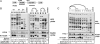
References
-
- Daley, G. Q., Goodell, M. A. & Snyder, E. Y. (2003) Hematology (Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program) 398-418. - PubMed
-
- Hochedlinger, K., Rideout, W. M., Kyba, M., Daley, G. Q., Blelloch, R. & Jaenisch, R. (2004) Hematol. J. 5, Suppl. 3, S114-S117. - PubMed
-
- Rideout, W. M., 3rd, Hochedlinger, K., Kyba, M., Daley, G. Q. & Jaenisch, R. (2002) Cell 109, 17-27. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
-
- Kyba, M. & Daley, G. Q. (2003) Exp. Hematol. 31, 994-1006. - PubMed
-
- Sauvageau, G., Thorsteinsdottir, U., Eaves, C. J., Lawrence, H. J., Largman, C., Lansdorp, P. M. & Humphries, R. K. (1995) Genes Dev. 9, 1753-1765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Substances
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

