Analysis of the cellular mechanism of antitumor responses and autoimmunity in patients treated with CTLA-4 blockade (VSports app下载)
- PMID: 16301685
- PMCID: PMC1473972
- DOI: V体育平台登录 - 10.4049/jimmunol.175.11.7746
Analysis of the cellular mechanism of antitumor responses and autoimmunity in patients treated with CTLA-4 blockade
"V体育2025版" Abstract
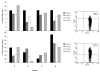
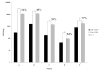
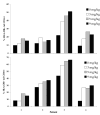
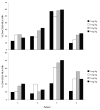
We have demonstrated previously that the administration of CTLA-4 blockade has mediated objective cancer regression and autoimmunity in patients with metastatic melanoma. To explore the mechanism of these in vivo effects, we have studied the changes in lymphocyte phenotype and function in patients receiving anti-CTLA-4 Ab (MDX-010). Patients with stage IV melanoma or renal cell cancer were treated every 3 wk with an anti-CTLA-4 Ab with or without peptide immunization VSports手机版. Pheresis samples were analyzed using flow cytometry to determine lymphocyte cell surface markers. Gene expression analyses and proliferation assays were conducted on purified T cell subsets. Anti-CTLA-4 Ab did not inhibit the suppressive activity of CD4+CD25+ cells in vitro or in vivo. In addition, there was no decrease in the expression of CD4+CD25+ cells in whole PBMC, nor a decrease in Foxp3 gene expression in the CD4+ or CD4+CD25+ purified cell populations posttreatment. The percentage of CD4+, CD8+, CD4+CD25+, and CD4+CD25- T cells in PBMC expressing the activation marker HLA-DR increased following anti-CTLA-4 Ab administration. Therefore, our results suggest that the antitumor effects of CTLA-4 blockade are due to increased T cell activation rather than inhibition or depletion of T regulatory cells. .
Figures
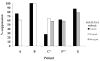
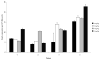
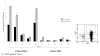
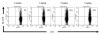
Comment in
-
Comment on "Analysis of the cellular mechanism of antitumor responses and autoimmunity in patients treated with CTLA-4 blockade".J Immunol. 2006 May 1;176(9):5136; author reply 5136. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.9.5136. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16621974 No abstract available.
V体育2025版 - References
-
- Egen JG, Kuhns MS, Allison JP. CTLA-4: new insights into its biological function and use in tumor immunotherapy. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:611–618. - PubMed
-
- Davis SJ, Ikemizu S, Evans EJ, Fugger L, Bakker TR, van der Merwe PA. The nature of molecular recognition by T cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:217–224. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz RH. T cell anergy. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:305–334. - PubMed
-
- Chambers CA, Kuhns MS, Egen JG, Allison JP. CTLA-4-mediated inhibition in regulation of T cell responses: mechanisms and manipulation in tumor immunotherapy. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:565–594. - "VSports app下载" PubMed
-
- Alegre ML, Frauwirth KA, Thompson CB. T cell regulation by CD28 and CTLA-4. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1:220–228. - PubMed
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Substances (VSports最新版本)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources (V体育官网入口)
VSports - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

