A genome-wide survey demonstrates widespread non-linear mRNA in expressed sequences from multiple species
- PMID: 16237125
- PMCID: V体育安卓版 - PMC1258171
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki893
A genome-wide survey demonstrates widespread non-linear mRNA in expressed sequences from multiple species
"V体育2025版" Abstract
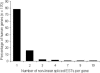
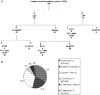
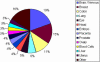
We describe here the results of the first genome-wide survey of candidate exon repetition events in expressed sequences from human, mouse, rat, chicken, zebrafish and fly. Exon repetition is a rare event, reported in <10 genes, in which one or more exons is tandemly duplicated in mRNA but not in the gene. To identify candidates, we analysed database sequences for mRNA transcripts in which the order of the spliced exons does not follow the linear genomic order of the individual gene [events we term rearrangements or repetition in exon order (RREO)]. Using a computational approach, we have identified 245 genes in mammals that produce RREO events. RREO in mRNA occurs predominantly in the coding regions of genes. However, exon 1 is never involved. Analysis of the open reading frames suggests that this process may increase protein diversity and regulate protein expression via nonsense-mediated RNA decay. The sizes of the exons and introns involved around these events suggest a gene model structure that may facilitate non-linear splicing VSports手机版. These findings imply that RREO affects a significant subset of genes within a genome and suggests that non-linear information encoded within the genomes of complex organisms could contribute to phenotypic variation. .
Figures

References
-
- Lander E.S., Linton L.M., Birren B., Nusbaum C., Zody M.C., Baldwin J., Devon K., Dewar K., Doyle M., FitzHugh W., et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Venter J.C., Adams M.D., Myers E.W., Li P.W., Mural R.J., Sutton G.G., Smith H.O., Yandell M., Evans C.A., Holt R.A., et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science. 2001;291:1304–1351. - PubMed
-
- Maniatis T., Tasic B. Alternative pre-mRNA splicing and proteome expansion in metazoans. Nature. 2002;418:236–243. - PubMed
-
- Modrek B., Lee C. A genomic view of alternative splicing. Nature Genet. 2002;30:13–19. - PubMed
-
- Johnson J., Castle J., Garrett-Engle P., Kan Z., Loerch P., Armour C., Santos R., Schadt E., Stoughton R., Shoemaker D. Genome-wide survey of human alternative pre-mRNA splicing with exon junction microarrays. Science. 2003;302:2141–2144. - VSports app下载 - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
VSports app下载 - MeSH terms
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
"VSports app下载" Substances
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

