General translational repression by activators of mRNA decapping
- PMID: 16179257
- PMCID: PMC1853273
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.012
General translational repression by activators of mRNA decapping
Abstract
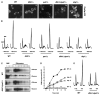
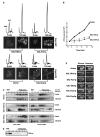
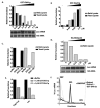
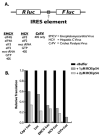
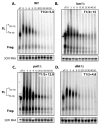
Translation and mRNA degradation are affected by a key transition where eukaryotic mRNAs exit translation and assemble an mRNP state that accumulates into processing bodies (P bodies), cytoplasmic sites of mRNA degradation containing non-translating mRNAs, and mRNA degradation machinery. We identify the decapping activators Dhh1p and Pat1p as functioning as translational repressors and facilitators of P body formation. Strains lacking both Dhh1p and Pat1p show strong defects in mRNA decapping and P body formation and are blocked in translational repression. Contrastingly, overexpression of Dhh1p or Pat1p causes translational repression, P body formation, and arrests cell growth. Dhh1p, and its human homolog, RCK/p54, repress translation in vitro, and Dhh1p function is bypassed in vivo by inhibition of translational initiation. These results identify a broadly acting mechanism of translational repression that targets mRNAs for decapping and functions in translational control VSports手机版. We propose this mechanism is competitively balanced with translation, and shifting this balance is an important basis of translational control. .
Figures

References
-
- Akao Y, Mizoguchi H, Ohishi N, Yagi K. Growth inhibition by overexpression of human DEAD box protein rck/p54 in cells of a guinea pig cell line. FEBS Lett. 1998;429:279–283. - VSports最新版本 - PubMed
-
- Andrei M, Ingelfinger D, Heintzmann R, Achsel T, Rivera-Pomar R, Luhrmann R. A role for eIF4E and eIF4E-transporter in targeting mRNPs to mammalian processing bodies. RNA. 2005;11:717–727. - "VSports注册入口" PMC - PubMed
VSports - Publication types
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
Substances
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports在线直播" Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

